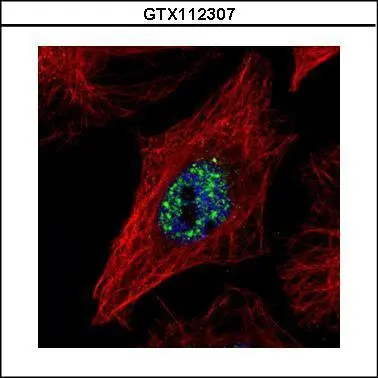
Confocal immunofluorescence analysis (Olympus FV10i) of paraformaldehyde-fixed HeLa, using NCOA2(GTX112307) antibody (Green) at 1:500 dilution. Alpha-tubulin filaments were labeled with GTX11304 (Red) at 1:2000.
NCOA2 antibody [C2C3], C-term
GTX112307
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetNCOA2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNCOA2 antibody [C2C3], C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
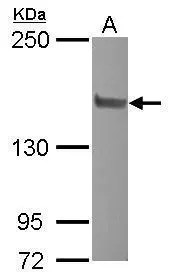
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID10499
- Target nameNCOA2
- Target descriptionnuclear receptor coactivator 2
- Target synonymsGRIP1, KAT13C, NCoA-2, SRC2, TIF2, bHLHe75, nuclear receptor coactivator 2, class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 75, glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein-1, p160 steroid receptor coactivator 2, transcriptional intermediary factor 2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ15596
- Protein NameNuclear receptor coactivator 2
- Scientific DescriptionThe NCOA2 gene encodes nuclear receptor coactivator 2, which aids in the function of nuclear hormone receptors. Nuclear hormone receptors are conditional transcription factors that play important roles in various aspects of cell growth, development, and homeostasis by controlling expression of specific genes. Members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily, which includes the 5 steroid receptors and class II nuclear receptors (see below), are structurally characterized by 3 distinct domains: an N-terminal transcriptional activation domain, a central DNA-binding domain, and a C-terminal hormone-binding domain. Before the binding of hormone, steroid receptors, which are sometimes called class I of the nuclear hormone receptor family, remain inactive in a complex with heat-shock protein-90 (MIM 140571) and other stress family proteins. Binding of hormone induces critical conformational changes in steroid receptors that cause them to dissociate from the inhibitory complex, bind as homodimers to specific DNA enhancer elements associated with target genes, and modulate that genes transcription. After binding to enhancer elements, transcription factors require transcriptional coactivator proteins to mediate their stimulation of transcription initiation (Hong et al., 1997 [PubMed 9111344]).[supplied by OMIM]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161