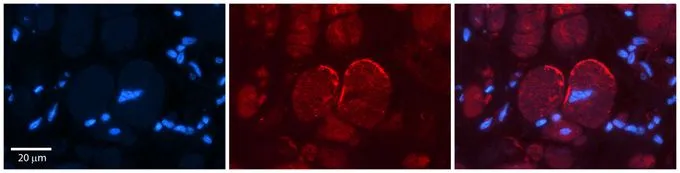
IHC-P analysis of human heart tissue using GTX47702 NMDAR2C antibody, N-term at 1:100. Left to right:DAPI, GRIN2C, Merge. Low pH, heat-induced antigen retrieval method utilizing Sodium Citrate buffer.
NMDAR2C antibody, N-term
GTX47702
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetGRIN2C
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNMDAR2C antibody, N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.2-2.5 ug/ml. IHC-P: 2-10 ug/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2905
- Target nameGRIN2C
- Target descriptionglutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 2C
- Target synonymsGluN2C, NMDAR2C, NR2C, glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C, GluN2C(alt_5'UTR_77nt), GluN2C(alt_5'UTR_87nt), GluN2C(del_e2), GluN2C-b alternative isoform, N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2C, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2C, glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-3, glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2C, putative NMDtranscript(altAcc_e11), putative NMDtranscript(altDon_e4), putative NMDtranscript(del_e4)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ14957
- Protein NameGlutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, which is a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptor. NMDA receptors are found in the central nervous system, are permeable to cations and have an important role in physiological processes such as learning, memory, and synaptic development. The receptor is a tetramer of different subunits (typically heterodimer of subunit 1 with one or more of subunits 2A-D), forming a channel that is permeable to calcium, potassium, and sodium, and whose properties are determined by subunit composition. Alterations in the subunit composition of the receptor are associated with pathophysiological conditions such as Parkinsons disease, Alzheimers disease, depression, and schizophrenia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161