Chemical Structure
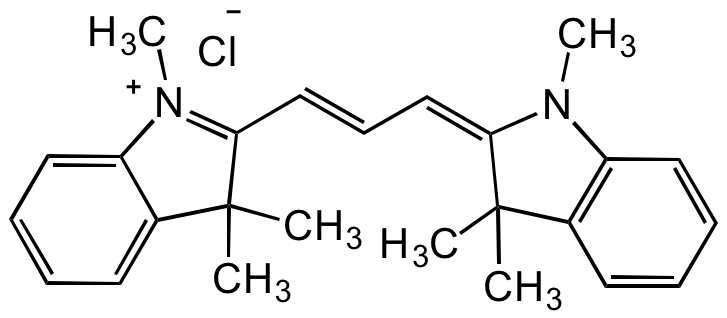
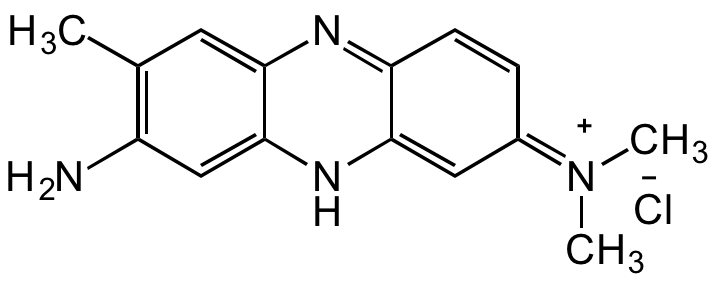
Neutral Red 5 [553-24-2]
CDX-N0249
CAS Number553-24-2
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight288.78
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameNeutral Red 5 [553-24-2]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number553-24-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Molecular FormulaC15H17CIN4
- Molecular Weight288.78
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 553-24-2. Formula: C15H17CIN4. MW: 288.78. Neutral red acts as a cellular pH indicator, changing from red to yellow between pH 6.8 and 8.0. More important, it is a dye used for staining in histology. It stains lysosomes red and is used as a general stain in histology, as a counterstain in combination with other dyes, and for many staining methods. It is applied in histology for nuclear staining, fluorescence staining, polychrome staining or for counter staining in Gram staining. It has also been incorporated in investigation of viruses, as a pH indicator, determination of DNA with optical and electrochemical methods, evalutaion of synthetic and naturally derived biomaterials. In microbiology, it is used in the MacConkey agar to differentiate bacteria for lactose fermentation. Neutral red is often used as a vital stain. Live cells incorporate neutral red into their lysosomes. As cells begin to die, their ability to incorporate neutral red diminishes. Thus, loss of neutral red uptake corresponds to loss of cell viability. The compound once taken up by cells can be used to acertain cell viability with a excitation maximum at 470nm and emission maximum at 580nm. Neutral red is added to some growth media for bacterial and cell cultures. Neutral red can be electrochemically polymerized and used as a redox mediator. - Neutral red acts as a cellular pH indicator, changing from red to yellow between pH 6.8 and 8.0. More important, it is a dye used for staining in histology. It stains lysosomes red and is used as a general stain in histology, as a counterstain in combination with other dyes, and for many staining methods. It is applied in histology for nuclear staining, fluorescence staining, polychrome staining or for counter staining in Gram staining. It has also been incorporated in investigation of viruses, as a pH indicator, determination of DNA with optical and electrochemical methods, evalutaion of synthetic and naturally derived biomaterials. In microbiology, it is used in the MacConkey agar to differentiate bacteria for lactose fermentation. Neutral red is often used as a vital stain. Live cells incorporate neutral red into their lysosomes. As cells begin to die, their ability to incorporate neutral red diminishes. Thus, loss of neutral red uptake corresponds to loss of cell viability. The compound once taken up by cells can be used to acertain cell viability with a excitation maximum at 470nm and emission maximum at 580nm. Neutral red is added to some growth media for bacterial and cell cultures. Neutral red can be electrochemically polymerized and used as a redox mediator.
- SMILESCC1=C(N)C=C(NC(C2=N3)=C/C(C=C2)=[N+](C)/C)C3=C1.[Cl-]
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12162000