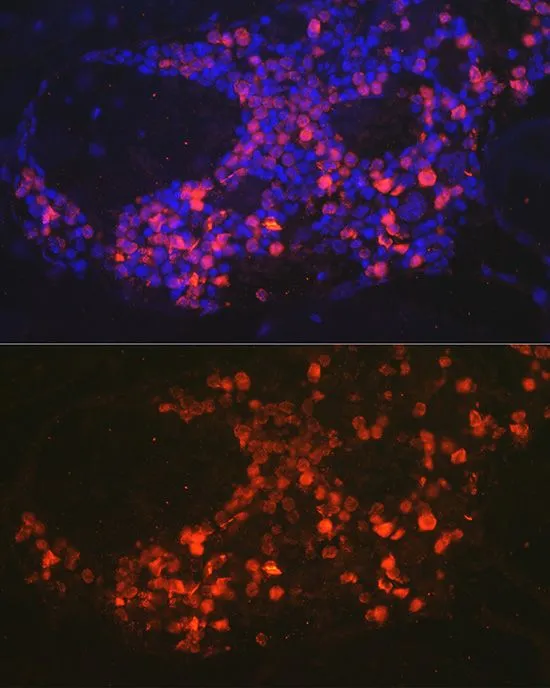
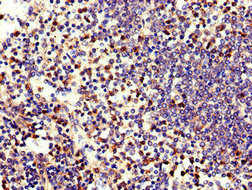
Neutrophil elastase antibody [NP57]
GTX72042
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetELANE
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNeutrophil elastase antibody [NP57]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC: Prolonged fixation in buffered formalin can destroy the epitope. The antibody may be used at a dilution of 1:50 to 1:150 with AutoProbe III (GTX28620). Dilute according to the particular application being used. In general, the 0.05M Borate pH 8.0 containing 0.15M Sodium Chloride, 0.05% Sodium Azide, is a good diluent to use with most antibodies. The optimal conditions should be determined by the individual laboratory.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDNP57
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1991
- Target nameELANE
- Target descriptionelastase, neutrophil expressed
- Target synonymsELA2, GE, HLE, HNE, NE, PMN-E, SCN1, neutrophil elastase, PMN elastase, bone marrow serine protease, elastase 2, neutrophil, elastase-2, granulocyte-derived elastase, leukocyte elastase, medullasin, polymorphonuclear elastase, polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP08246
- Protein NameNeutrophil elastase
- Scientific DescriptionElastases form a subfamily of serine proteases that hydrolyze many proteins in addition to elastin. Humans have six elastase genes which encode structurally similar proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the active protease. Following activation, this protease hydrolyzes proteins within specialized neutrophil lysosomes, called azurophil granules, as well as proteins of the extracellular matrix. The enzyme may play a role in degenerative and inflammatory diseases through proteolysis of collagen-IV and elastin. This protein also degrades the outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of E. coli as well as the virulence factors of such bacteria as Shigella, Salmonella and Yersinia. Mutations in this gene are associated with cyclic neutropenia and severe congenital neutropenia (SCN). This gene is present in a gene cluster on chromosome 19. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

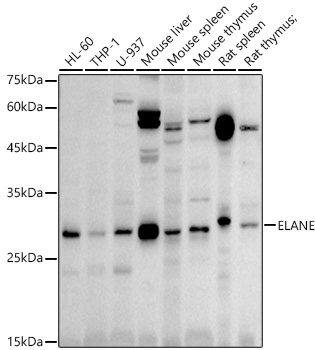


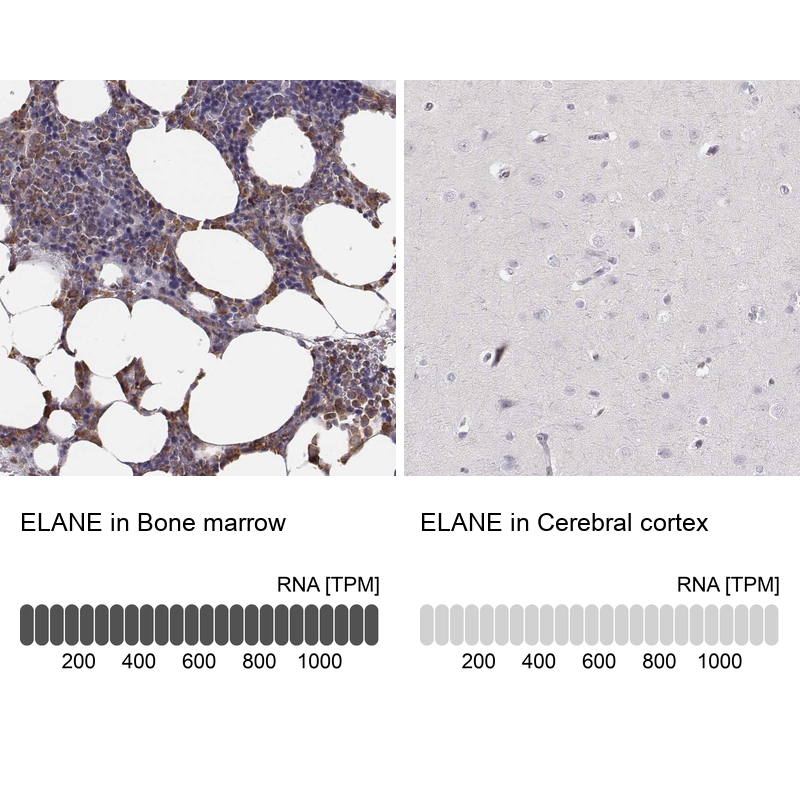
![WB analysis of mouse spleen tissue lysate using GTX05032 Neutrophil elastase antibody [AOCI-5]. Dilution : 1:5000](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX05032/GTX05032_20241225_WB_1_24122500_977.webp)