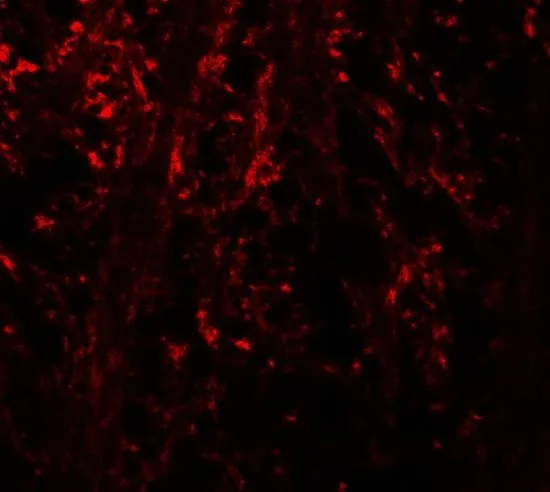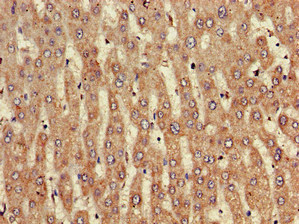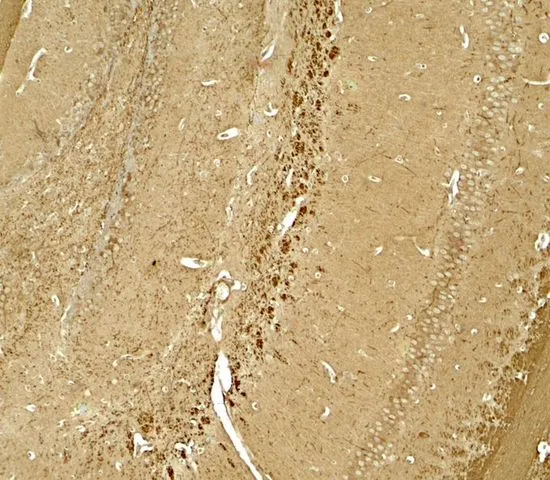
IHC-P analysis of mouse brain tissue using GTX31596 NINJ1 antibody. Working concentration : 5 μg/ml
NINJ1 antibody
GTX31596
ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetNINJ1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNINJ1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 5 microg/mL. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4814
- Target nameNINJ1
- Target descriptionninjurin 1
- Target synonymsNIN1, NINJURIN, hNINJ1, ninjurin-1, nerve injury-induced protein-1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ92982
- Protein NameNinjurin-1
- Scientific DescriptionThe ninjurin protein is upregulated after nerve injury both in dorsal root ganglion neurons and in Schwann cells (Araki and Milbrandt, 1996 [PubMed 8780658]). It demonstrates properties of a homophilic adhesion molecule and promotes neurite outgrowth from primary cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons.[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2009]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Tomo-seq identifies NINJ1 as a potential target for anti-inflammatory strategy in thoracic aortic dissection.Read this paper
- Single-cell sequencing reveals homogeneity and heterogeneity of the cytopathological mechanisms in different etiology-induced AKI.Read this paper