Chemical Structure
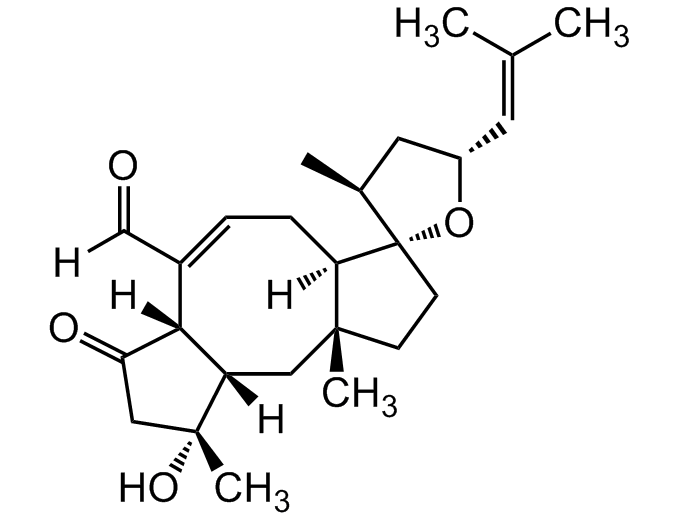
Ophiobolin A [4611-05-6] [4611-05-6]
AG-CN2-0431
CAS Number4611-05-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight400.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameOphiobolin A [4611-05-6] [4611-05-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number4611-05-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC25H36O4
- Molecular Weight400.6
- Scientific DescriptionCell permeable, irreversible calmodulin antagonist. Acts by covalently binding to a lysine-rich inhibitory site. Inhibits by blocking the activation of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase [1-3, 5, 6, 9]. Herbicidal mycotoxin [7]. Phytotoxic, antifungal, antibacterial and nematocidal compound [4, 6, 10]. Anticancer compound. Shown to induce paraptosis-like cell death [11, 12]. Shown to inhibit P-glycoprotein-mediated transport [8]. Disruptor of intracellular sulfhydryl proteostasis, leading to ER stress and dilation. - Chemical. CAS: 4611-05-6. Formula: C25H36O4. MW: 400.6. Isolated from Bipolaris leersia. Cell permeable, irreversible calmodulin antagonist. Acts by covalently binding to a lysine-rich inhibitory site. Inhibits by blocking the activation of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. Herbicidal mycotoxin. Phytotoxic, antifungal, antibacterial and nematocidal compound. Anticancer compound. Shown to induce paraptosis-like cell death. Shown to inhibit P-glycoprotein-mediated transport.
- SMILES[H]C(=O)C1=C[C@]2([H])[C@](C)(CC[C@@]22O[C@H](C[C@@H]2C)C=C(C)C)C[C@@]2([H])[C@]1([H])C(=O)C[C@@]2(C)O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UN NumberUN 3462
- UNSPSC12352200

![Ophiobolin A [4611-05-6] [4611-05-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/8A/CgoaEWayI-KEbcA4AAAAAJpNCLo497.png)