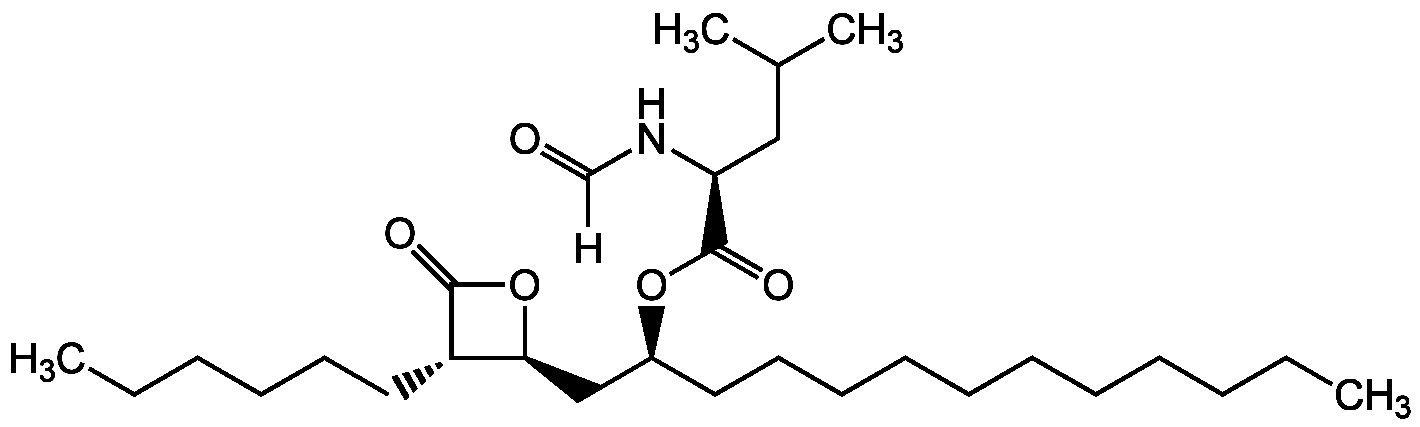
Chemical Structure
Orlistat [96829-58-2] [96829-58-2]
AG-CN2-0050
CAS Number96829-58-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight495.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameOrlistat [96829-58-2] [96829-58-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number96829-58-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC29H53NO5
- Molecular Weight495.7
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 96829-58-2. Formula: C29H53NO5. MW: 495.7. Synthetic. Originally isolated from Streptomyces sp. Hypolipemic cell permeable and irreversible pancreatic, gastric and carboxylester lipase inhibitor. Anti-obesity and antihypercholesterolemic compound. Antitumor compound by inhibition of the thioesterase domain of fatty acid synthase (FASN). Anti-proliferative. Causes cell cycle arrest at G1 phase. Apoptosis inducer through caspase-3 activation. Sn-1-selective-diacylglycerol lipases alpha (DAGLalpha) inhibitor. Targets serine hydrolases in the nervous system, such as diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL), which is responsible for the conversion of DAG to 2-AG. Partially inhibits the hydrolysis of triglycerides and lowers the absorption of dietary fat, promoting weight loss. Promotes the sensitivity to TRAIL in cancer cells by ROS-mediated pathways. - Hypolipemic cell permeable and irreversible pancreatic, gastric and carboxylester lipase inhibitor [1-3]. Anti-obesity and antihypercholesterolemic compound [2, 5, 11]. Antitumor compound by inhibition of the thioesterase domain of fatty acid synthase (FASN) [4, 6, 9, 10]. Anti-proliferative [4, 6, 9, 10]. Causes cell cycle arrest at G1 phase. Apoptosis inducer through caspase-3 activation [6, 10]. Sn-1-selective-diacylglycerol lipases alpha (DAGLalpha) inhibitor. Targets serine hydrolases in the nervous system, such as diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL), which is responsible for the conversion of DAG to 2-AG [7]. Partially inhibits the hydrolysis of triglycerides and lowers the absorption of dietary fat, promoting weight loss [8]. Promotes the sensitivity to TRAIL in cancer cells by ROS-mediated pathways [11].
- SMILES[H]C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)O[C@@H](CCCCCCCCCCC)C[C@@H]1OC(=O)[C@H]1CCCCCC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Orlistat [96829-58-2] [96829-58-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/D7/CgoaEWY7Og6EEWahAAAAANt4Ne8290.png)