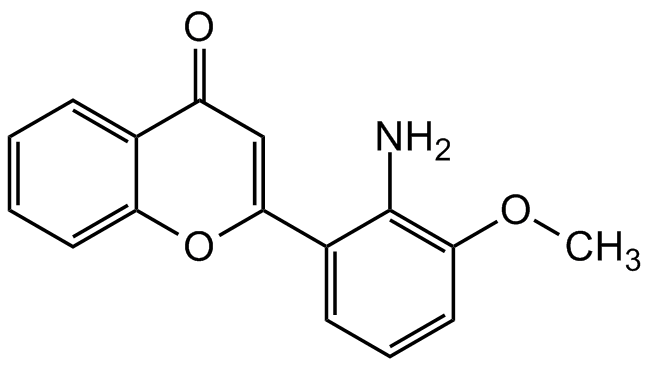
Chemical Structure
PD 98,059 [167869-21-8] [167869-21-8]
AG-CR1-0118
CAS Number167869-21-8
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight267.3
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NamePD 98,059 [167869-21-8] [167869-21-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number167869-21-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC16H13NO3
- Molecular Weight267.3
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 167869-21-8. Formula: C16H13NO3. MW: 267.3. Highly selective, reversible and cell permeable MEK (MAP kinase kinase) inhibitor. Blocks the phosphorylation and activation of the MAP kinase pathway. T cell activation inhibitor. Inhibits cell growth and cell proliferation of several cancer cells. - Highly selective, reversible and cell permeable MEK (MAP kinase kinase) inhibitor [1-3, 7]. Blocks the phosphorylation and activation of the MAP kinase pathway [1-3, 7]. T cell activation inhibitor [4]. Inhibits cell growth and cell proliferation of several cancer cells [5, 6, 8].
- SMILESCOC1=C(N)C(=CC=C1)C1=CC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2O1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![PD98059 [167869-21-8] [167869-21-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/3E/CgoaEWayGhSEfyLQAAAAAAiVPkY243.png)