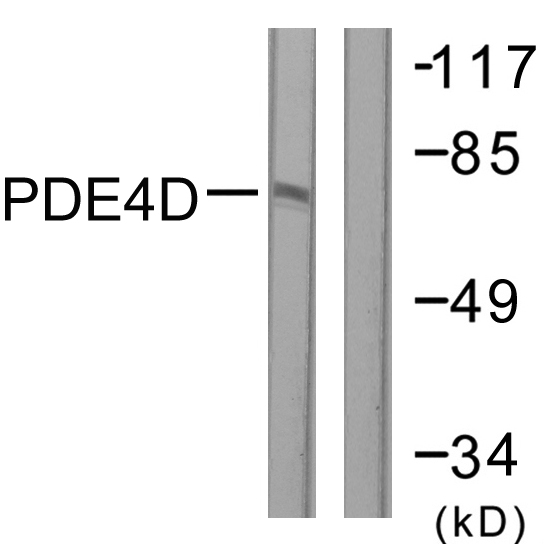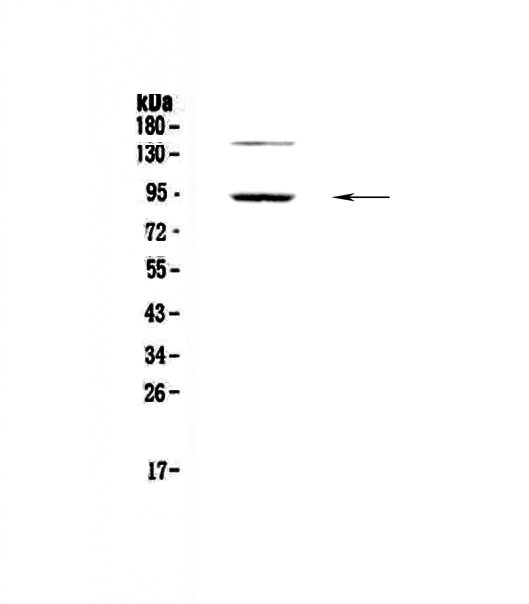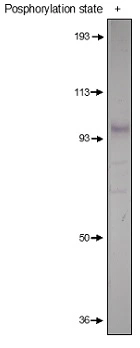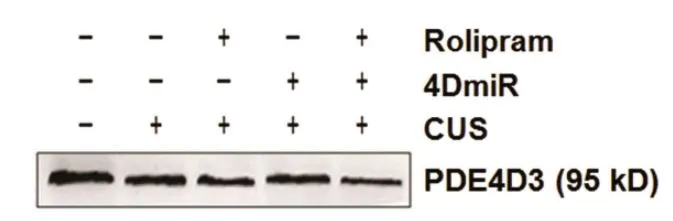
WB analysis of mouse prefrontal cortical tissue lysate using GTX14614 PDE4D3 antibody.
PDE4D3 antibody
GTX14614
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityChicken, Mouse, Rat
TargetPDE4D
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NamePDE4D3 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500. ICC/IF: 1:200. IP: 1:150. ELISA: 1:10000. IHC: 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.68 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID5144
- Target namePDE4D
- Target descriptionphosphodiesterase 4D
- Target synonymsACRDYS2, DPDE3, HSPDE4D, PDE43, PDE4DN2, STRK1, 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase 4D, cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4D, cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D6, phosphodiesterase 4D, cAMP-specific (phosphodiesterase E3 dunce homolog, Drosophila), testicular tissue protein Li 136
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ08499
- Protein Name3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase 4D
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes one of four mammalian counterparts to the fruit fly dunce gene. The encoded protein has 3,5-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity and degrades cAMP, which acts as a signal transduction molecule in multiple cell types. This gene uses different promoters to generate multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode functional proteins.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]
- ReactivityChicken, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Phosphodiesterase-4D knock-out and RNA interference-mediated knock-down enhance memory and increase hippocampal neurogenesis via increased cAMP signaling. Li YF et al., 2011 Jan 5, J NeurosciRead this paper