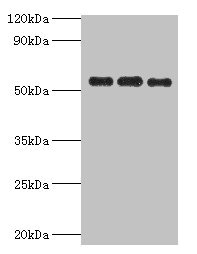
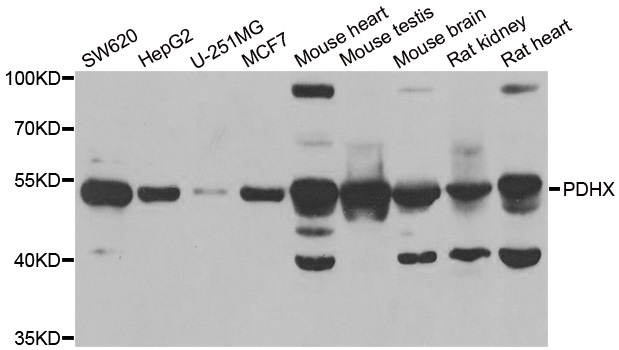
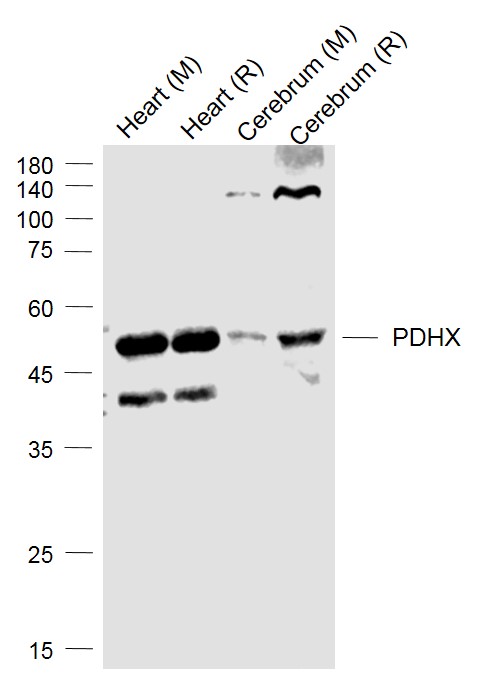
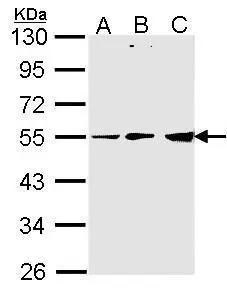
PDHX Polyclonal Antibody
RD83813A
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetPDHX
Overview
- SupplierReddot Biotech
- Product NamePDHX Polyclonal Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer5
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID8050
- Target namePDHX
- Target descriptionpyruvate dehydrogenase complex component X
- Target synonymsDLDBP, E3BP, OPDX, PDHXD, PDX1, proX, pyruvate dehydrogenase protein X component, mitochondrial, dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase-binding protein of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, lipoyl-containing pyruvate dehydrogenase complex component X, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, E3-binding protein subunit, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, lipoyl-containing component X
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionThe pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex is located in the mitochondrial matrix and catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A. The PDH complex thereby links glycolysis to Krebs cycle. The PDH complex contains three catalytic subunits, E1, E2, and E3, two regulatory subunits, E1 kinase and E1 phosphatase, and a non-catalytic subunit, E3 binding protein (E3BP). This gene encodes the E3 binding protein subunit; also known as component X of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. This protein tethers E3 dimers to the E2 core of the PDH complex. Defects in this gene are a cause of pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency which results in neurological dysfunction and lactic acidosis in infancy and early childhood. This protein is also a minor antigen for antimitochondrial antibodies. These autoantibodies are present in nearly 95% of patients with the autoimmune liver disease primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). In PBC, activated T lymphocytes attack and destroy epithelial cells in the bile duct where this protein is abnormally distributed and overexpressed. PBC eventually leads to cirrhosis and liver failure. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203