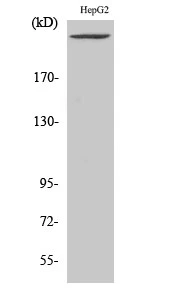
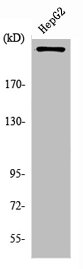
WB analysis of HepG2 cell lysate using GTX34124 PIKfyve antibody.
PIKfyve antibody
GTX34124
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPIKFYVE
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NamePIKfyve antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:2000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID200576
- Target namePIKFYVE
- Target descriptionphosphoinositide kinase, FYVE-type zinc finger containing
- Target synonymsCFD, FAB1, HEL37, PIP5K, PIP5K3, ZFYVE29, 1-phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase, PIPkin-III, epididymis luminal protein 37, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase type III, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate/phosphatidylinositol 5-kinase, type III, phosphoinositide kinase, FYVE finger containing, serine-protein kinase PIKFYVE, type III PIP kinase, zinc finger, FYVE domain containing 29
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9Y2I7
- Protein Name1-phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase
- Scientific DescriptionPhosphorylated derivatives of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) regulate cytoskeletal functions, membrane trafficking, and receptor signaling by recruiting protein complexes to cell- and endosomal-membranes. Humans have multiple PtdIns proteins that differ by the degree and position of phosphorylation of the inositol ring. This gene encodes an enzyme (PIKfyve; also known as phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase type III or PIPKIII) that phosphorylates the D-5 position in PtdIns and phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PtdIns3P) to make PtdIns5P and PtdIns(3,5)biphosphate. The D-5 position also can be phosphorylated by type I PtdIns4P-5-kinases (PIP5Ks) that are encoded by distinct genes and preferentially phosphorylate D-4 phosphorylated PtdIns. In contrast, PIKfyve preferentially phosphorylates D-3 phosphorylated PtdIns. In addition to being a lipid kinase, PIKfyve also has protein kinase activity. PIKfyve regulates endomembrane homeostasis and plays a role in the biogenesis of endosome carrier vesicles from early endosomes. Mutations in this gene cause corneal fleck dystrophy (CFD); an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by numerous small white flecks present in all layers of the corneal stroma. Histologically, these flecks appear to be keratocytes distended with lipid and mucopolysaccharide filled intracytoplasmic vacuoles. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161




![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with PIKfyve antibody [HL3158] (GTX640668) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Corresponding RNA expression data for the same cell lines are based on Human Protein Atlas program.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX640668/GTX640668_T-45481_20240729_WB_TPM_watermark_24080622_747.webp)
![Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with PIKfyve antibody [HL3449] (GTX641322) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX641322/GTX641322_T-45593_20241220_WB_M_tissue_24122400_689.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with PIKfyve antibody [HL3510] (GTX641398) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Corresponding RNA expression data for the same cell lines are based on Human Protein Atlas program.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX641398/GTX641398_T-45607_20241206_WB_TPM_watermark_24121100_746.webp)
