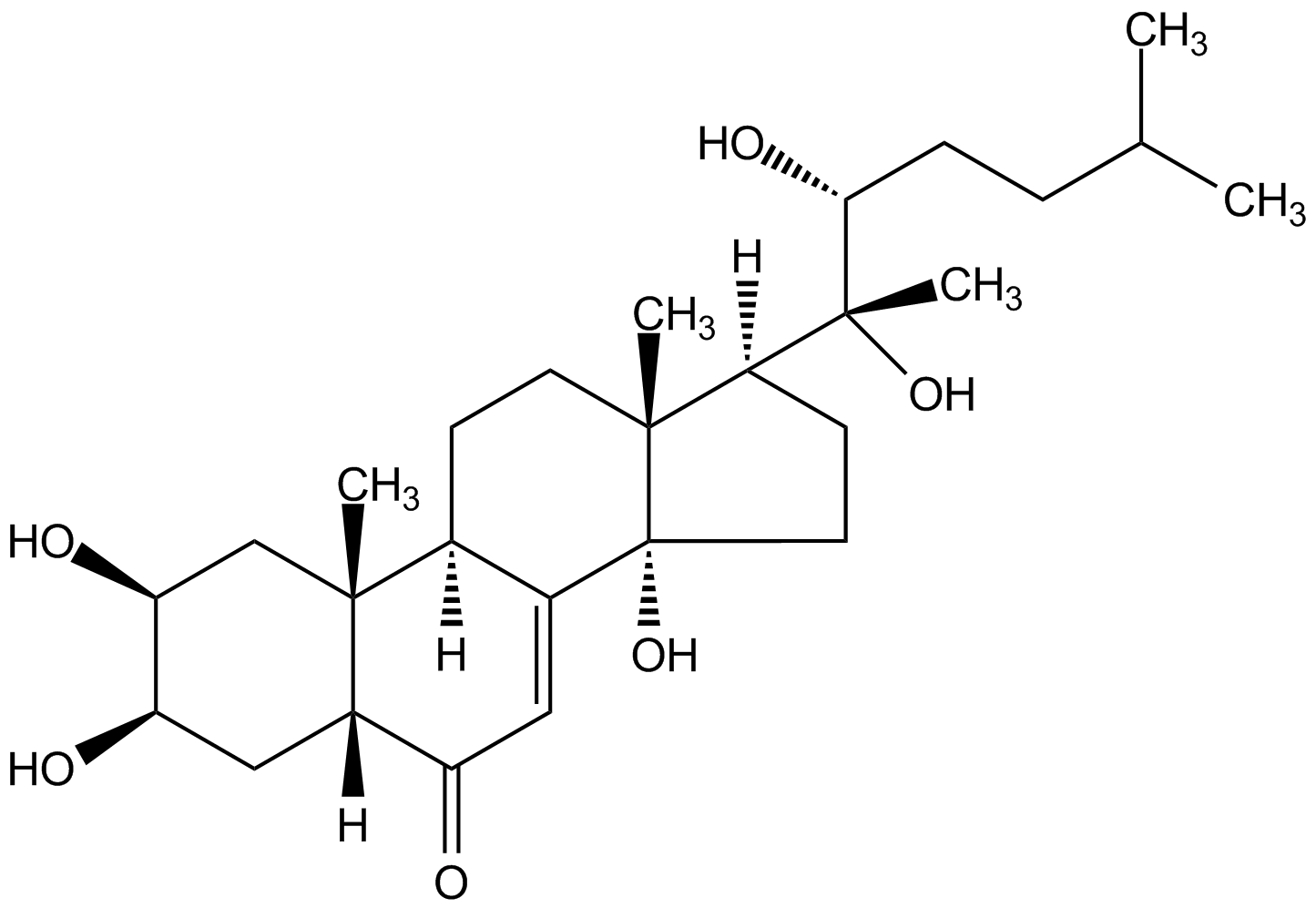
Chemical Structure
Ponasterone A [13408-56-5] [13408-56-5]
AG-CN2-0053
CAS Number13408-56-5
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight464.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NamePonasterone A [13408-56-5] [13408-56-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number13408-56-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC27H44O6
- Molecular Weight464.6
- Scientific DescriptionA member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Analog of ecdysone with similar properties to muristerone A. Functional, reliable and economical substitute for muristerone A as an inducer for the ecdysone-inducible mammalian expression system. Induces expression of beta-galactosidase to levels similar to those obtained with muristerone A induction. Potent compound for ecdysteroid activity. Insect steroid hormone involved in regulating metamorphosis. - Chemical. CAS: 13408-56-5. Formula: C27H44O6. MW: 464.6. Semi-synthetic. A member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Analog of ecdysone with similar properties to muristerone A. Functional, reliable and economical substitute for muristerone A as an inducer for the ecdysone-inducible mammalian expression system. Induces expression of beta-galactosidase to levels similar to those obtained with muristerone A induction. Potent compound for ecdysteroid activity. Insect steroid hormone involved in regulating metamorphosis.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2(O)C3=CC(=O)[C@]4([H])C[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@@](C)(O)[C@H](O)CCC(C)C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Ponasterone A [13408-56-5] [13408-56-5]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/7C/CgoaEWayIWOEfSNnAAAAAFYQWS8841.png)