PSMC5 antibody [25D5]
GTX70288
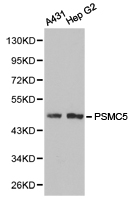
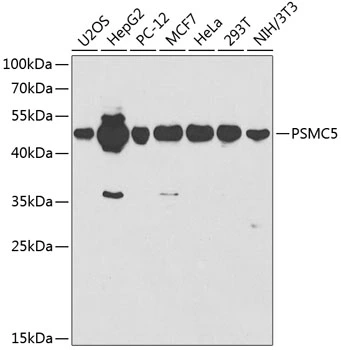
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
TargetPSMC5
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NamePSMC5 antibody [25D5]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID25D5
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID5705
- Target namePSMC5
- Target descriptionproteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 5
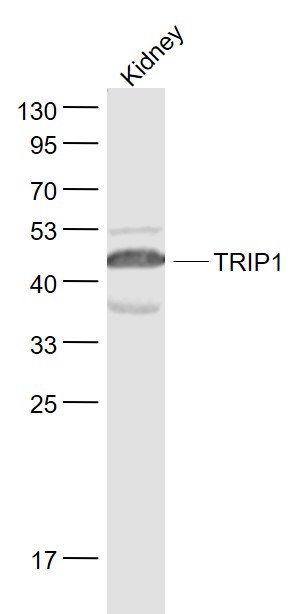
- Target synonymsRPT6, S8, SUG-1, SUG1, TBP10, TRIP1, p45, p45/SUG, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 8, 26S protease regulatory subunit 8, 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit RPT6, MSUG1 protein, Tat-binding protein homolog 10, proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, ATPase, 5, proteasome 26S ATPase subunit 5, proteasome subunit p45, testicular tissue protein Li 149, thyroid hormone receptor-interacting protein 1, thyroid receptor interactor 1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP62195
- Protein Name26S proteasome regulatory subunit 8
- Scientific DescriptionThe 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes one of the ATPase subunits, a member of the triple-A family of ATPases which have a chaperone-like activity. In addition to participation in proteasome functions, this subunit may participate in transcriptional regulation since it has been shown to interact with the thyroid hormone receptor and retinoid X receptor-alpha. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Mooser C, Symeonidou IE, Leimbacher PA, et al. Treacle controls the nucleolar response to rDNA breaks via TOPBP1 recruitment and ATR activation. Nat Commun. 2020,11(1):123. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13981-xRead this paper