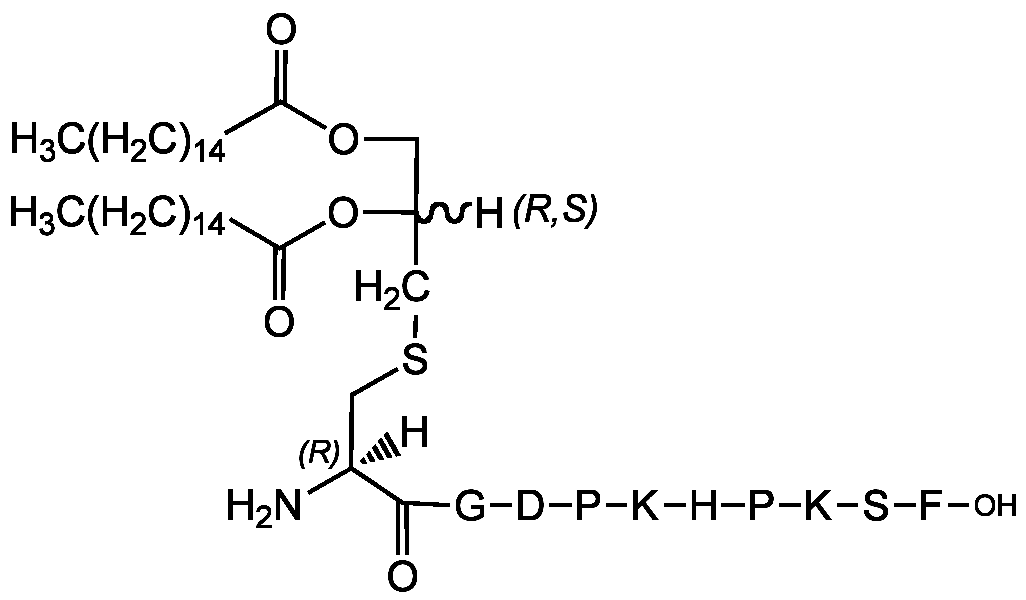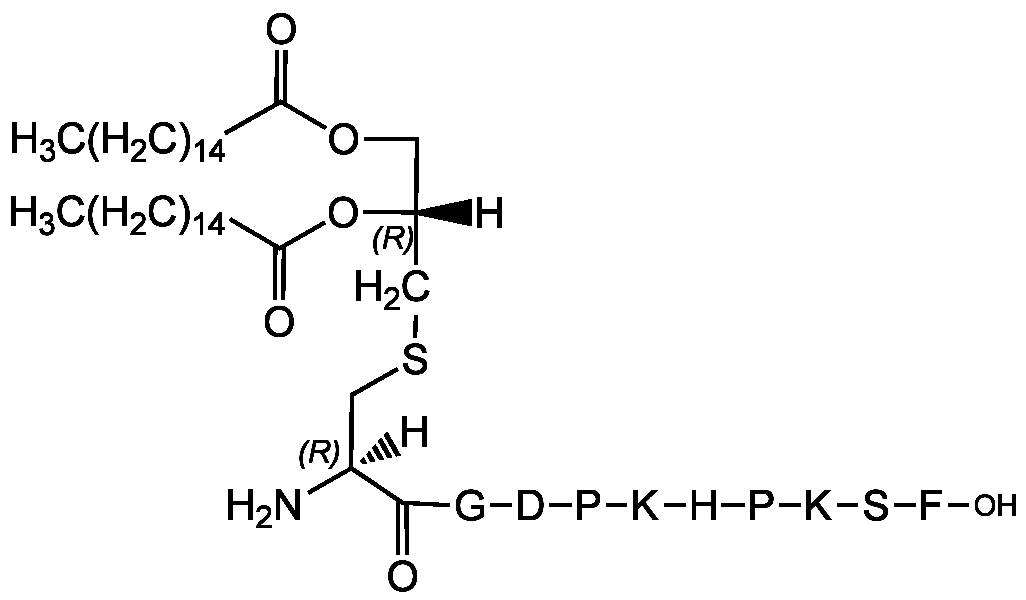
Chemical Structure
(R)-FSL-1
AG-CP3-0010
Molecular Weight1666.2
Product group Chemicals
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Name(R)-FSL-1
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Molecular FormulaC84H140N14O18S
- Molecular Weight1666.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. Formula: C84H140N14O18S. MW: 1666.2. Synthetic. R-FSL-1 (R-Pam2CGDPKHPKSF) is a synthetic lipoprotein that represents the N-terminal part of the 44kDa lipoprotein LP44 of Mycoplasma salivarium. The naturally occurring R-stereoisomer is biologically more active than the S-stereoisomer. Stimulator of TLR2/TLR6. Inducer of TNF-alpha production in macrophages. Upregulates proinflammatory cytokines. Activator of the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-kappaB. - R-FSL-1 (R-Pam2CGDPKHPKSF) is a synthetic lipoprotein that represents the N-terminal part of the 44kDa lipoprotein LP44 of Mycoplasma salivarium [1]. The naturally occurring R-stereoisomer is biologically more active than the S-stereoisomer [4]. Stimulator of TLR2/TLR6 [2-13]. Inducer of TNF-alpha production in macrophages [5]. Upregulates proinflammatory cytokines [3,5]. Activator of the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-kappaB [3].
- SMILES[H][C@@](COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)(CSC[C@]([H])(N)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(O)=O)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200