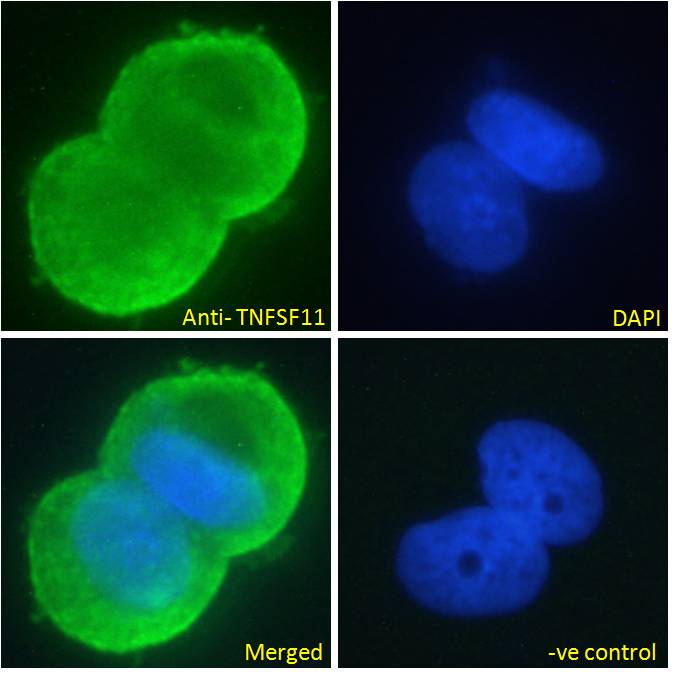
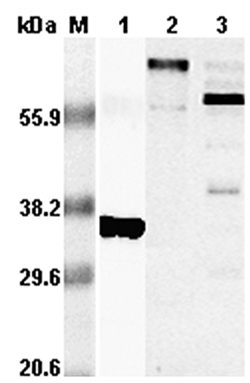
![RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term detects RANKL protein by western blot analysis. A. 50 μg rat lung extract 10% SDS-PAGE RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108515) dilution: 1:1000 The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term detects RANKL protein by western blot analysis. A. 50 μg rat lung extract 10% SDS-PAGE RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108515) dilution: 1:1000 The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108515/GTX108515_39812_WB_R_lung_w_23060120_271.webp)
RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term detects RANKL protein by western blot analysis. A. 50 μg rat lung extract 10% SDS-PAGE RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108515) dilution: 1:1000 The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term
GTX108515
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetTNFSF11
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameRANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID8600
- Target nameTNFSF11
- Target descriptionTNF superfamily member 11
- Target synonymsCD254, ODF, OPGL, OPTB2, RANKL, TNLG6B, TRANCE, hRANKL2, sOdf, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, TNF-related activation-induced cytokine, osteoclast differentiation factor, osteoprotegerin ligand, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand, tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11, tumor necrosis factor ligand 6B, tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 11
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO14788
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. This protein was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. This protein was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis. Targeted disruption of the related gene in mice led to severe osteopetrosis and a lack of osteoclasts. The deficient mice exhibited defects in early differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and failed to form lobulo-alveolar mammary structures during pregnancy. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

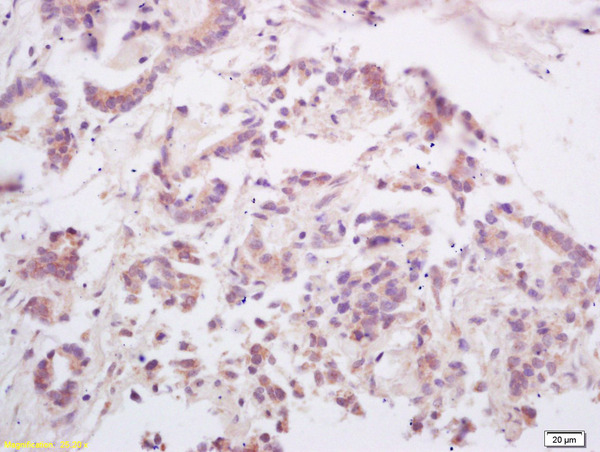
![RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term detects RANKL protein at membrane on human breast carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma. RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108515) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term detects RANKL protein at membrane on human breast carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma. RANKL antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108515) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108515/GTX108515_39812_20150123_IHC_w_23060120_120.webp)