Chemical Structure
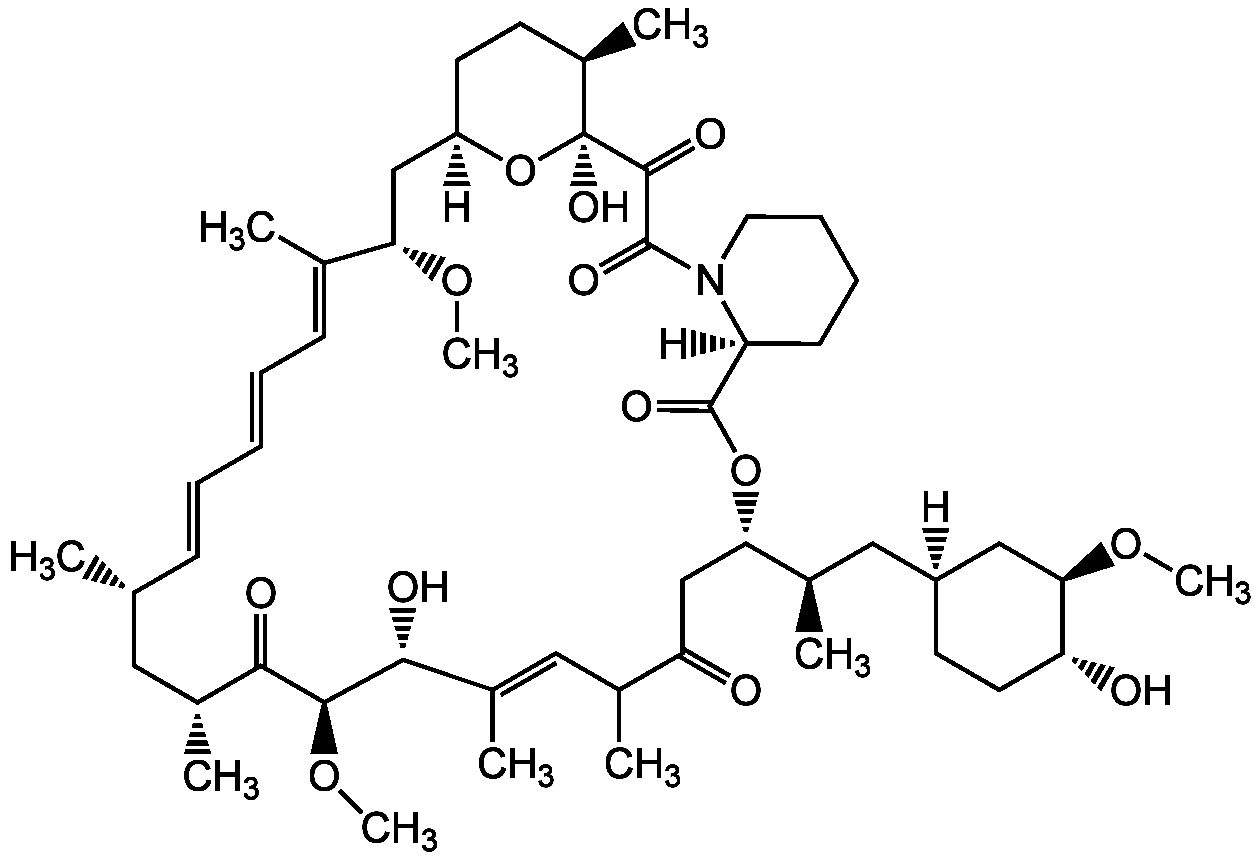
Rapamycin
AG-CN2-0025
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameRapamycin
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number53123-88-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC51H79NO13
- Molecular Weight914.2
- Scientific DescriptionAntibiotic. Antibacterial and antifungal properties [1, 2]. Forms a complex with FKBP12 and inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Inhibits the response to interleukin-2 (IL-2), and thereby blocks activation of T and B cells [3, 5, 6, 11]. Potent immunosuppressant [4, 10] used as an alternative to calcineurin inhibitors [12]. Restricts the proliferation of smooth-muscle cells by blocking cell cycle progression at the G1/S transition [7, 13]. Anti-proliferative. Antitumor compound [14, 15]. Apoptosis enhancer. Activator of autophagy both in vitro and in vivo [8, 9]. Anti-HIV and anti-aging compound [16, 17]. Neuroprotective [18]. Suppressor for self-renewal and vascular differentiation potential in hemangioma stem cells [19]. mTORC1 inhibitor [20]. - Chemical. CAS: 53123-88-9. Formula: C51H79NO13. MW: 914.2. Isolated from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Antibiotic. Antibacterial and antifungal properties. Forms a complex with FKBP12 and inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Inhibits the response to interleukin-2 (IL-2), and thereby blocks activation of T and B cells. Potent immunosuppressant used as an alternative to calcineurin inhibitors. Restricts the proliferation of smooth-muscle cells by blocking cell cycle progression at the G1/S transition. Anti-proliferative. Antitumor compound. Apoptosis enhancer. Activator of autophagy both in vitro and in vivo. Anti-HIV and anti-aging compound. Neuroprotective. Suppressor for self-renewal and vascular differentiation potential in hemangioma stem cells.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(C[C@@H](C)[C@@H]2CC(=O)C(C)\C=C(C)\[C@@H](O)[C@@H](OC)C(=O)[C@H](C)C[C@H](C)\C=C\C=C\C=C(C)\[C@H](C[C@@]3([H])CC[C@@H](C)[C@](O)(O3)C(=O)C(=O)N3CCCC[C@@]3([H])C(=O)O2)OC)CC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C1)OC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Rapamycin [53123-88-9]](https://bpsbioscience.com/media/catalog/product/2/7/27062_structure.png)

![Rapamycin [53123-88-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/3C/CgoaEGayGTyEWcytAAAAABbpRS0448.png)