WB analysis of GTX00360-pro Rat GDF8 / Myostatin protein.
Rat GDF8 / Myostatin protein, His tag
GTX00360-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDO35312
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameRat GDF8 / Myostatin protein, His tag
- Delivery Days Customer9
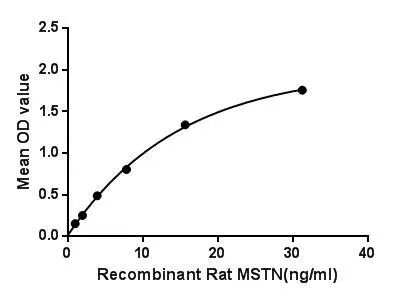
- Application Supplier NoteMyostatin (MSTN) also known as growth differentiation factor 8 (GDF-8) a myokine, a protein produced and released by myocytes. It inhibit myogenesis including muscle cell growth and differentiation. Myostatin is a secreted growth differentiation factor that is a member of the TGF beta protein family. Besides, Follistatin Like Protein 3 (FSTL3) has been identified as an interactor of MSTN, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant rat MSTN and recombinant rat FSTL3. Briefly, MSTN were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 microl were then transferred to FSTL3-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37C. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-MSTN pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37C. Finally, add 50 microl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of MSTN and FSTL3 was in a dose dependent manner.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Protein IDO35312
- Protein NameGrowth/differentiation factor 8
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) family of proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate an N-terminal propeptide and a C-terminal subunit. The C-terminal subunits form the mature homodimer, which negatively regulates skeletal muscle cell proliferation and differentiation. Mutations in this gene are associated with increased skeletal muscle mass in humans and other mammals. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352202