Chemical Structure
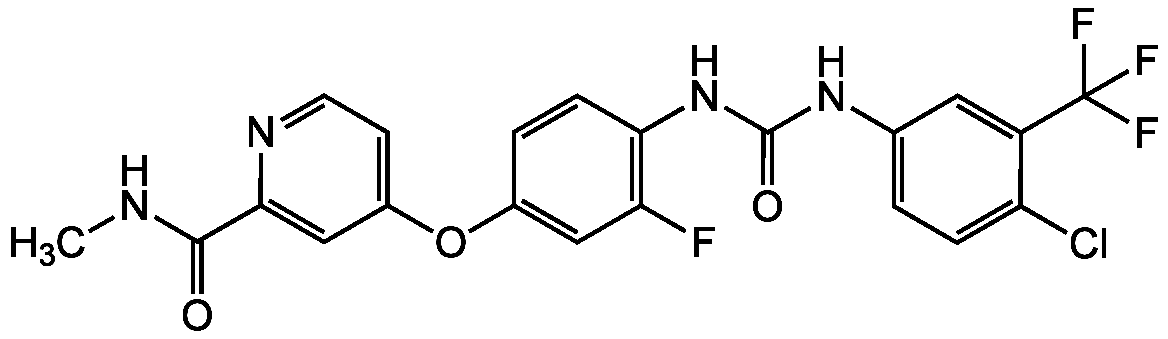
Regorafenib [BAY 73-4506] [755037-03-7]
AG-CR1-3623
CAS Number755037-03-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight482.8
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameRegorafenib [BAY 73-4506] [755037-03-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number755037-03-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC21H15ClF4N4O3
- Molecular Weight482.8
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 755037-03-7. Formula: C21H15ClF4N4O3. MW: 482.8. Orally bioavailable potent antitumor, antiangiogenic, antiproliferative and antineoplastic agent. Multi-target kinase inhibitor of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFRbeta, Kit, RET and Raf-1 with IC50 values of 13, 4.2, 46, 22, 7, 1.5 and 2.5nM, respectively. - Orally bioavailable potent antitumor, antiangiogenic, antiproliferative and antineoplastic agent. Multi-target kinase inhibitor of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFRbeta, Kit, RET and Raf-1 with IC50 values of 13, 4.2, 46, 22, 7, 1.5 and 2.5nM, respectively.
- SMILESCNC(=O)C1=CC(OC2=CC(F)=C(NC(=O)NC3=CC=C(Cl)C(=C3)C(F)(F)F)C=C2)=CC=N1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200