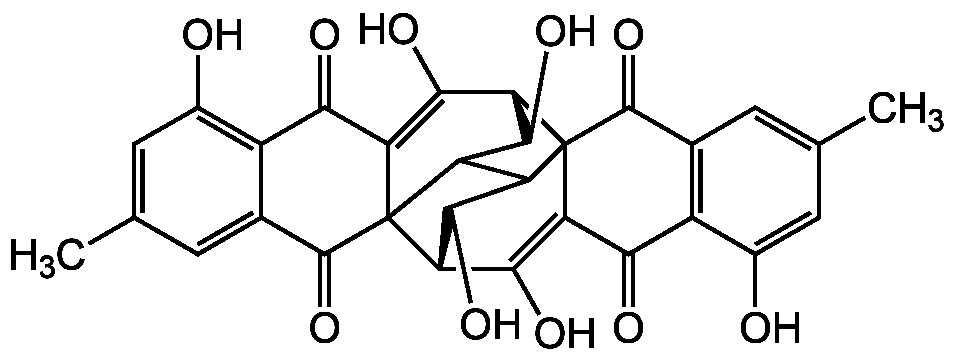
Chemical Structure
Rugulosin [23537-16-8] [23537-16-8]
AG-CN2-0124
CAS Number23537-16-8
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight542.5
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameRugulosin [23537-16-8] [23537-16-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number23537-16-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC30H22O10
- Molecular Weight542.5
- Scientific DescriptionAntibiotic [1]. Antibacteriophage. Antiviral [2]. Mycotoxin [3]. DNA replication, transcription and repair inhibitor [4]. Antibacterial [5]. RNA polymerase and ribonuclease H inhibitor [6]. Insecticidal. Cytotoxic [7]. HIV-1 integrase inhibitor [8]. Shows anti-MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) activity [9]. Potential Hsp90 inhibitor through interacting with N-Hsp90 [10]. - Chemical. CAS: 23537-16-8. Formula: C30H22O10. MW: 542.5. Isolated from Penicillium sp. Antibiotic. Antibacteriophage. Antiviral. Mycotoxin. DNA replication, transcription and repair inhibitor. Antibacterial. RNA polymerase and ribonuclease H inhibitor. Insecticidal. Cytotoxic. HIV-1 integrase inhibitor. Shows anti-MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) activity. Potential Hsp90 inhibitor through interacting with N-Hsp90.
- SMILESCC1=CC2=C(C(O)=C1)C(=O)C1=C(O)[C@H]3C(O)C4C5C(O)[C@H](C(O)=C6C(=O)C7=C(O)C=C(C)C=C7C(=O)C356)C14C2=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

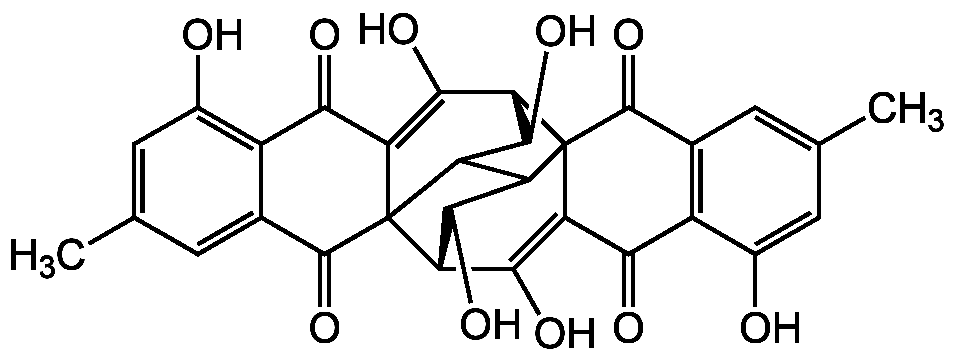

![Rugulosin [23537-16-8] [23537-16-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/D8/CgoaEGayRHOEZxV7AAAAANngHAU493.png)