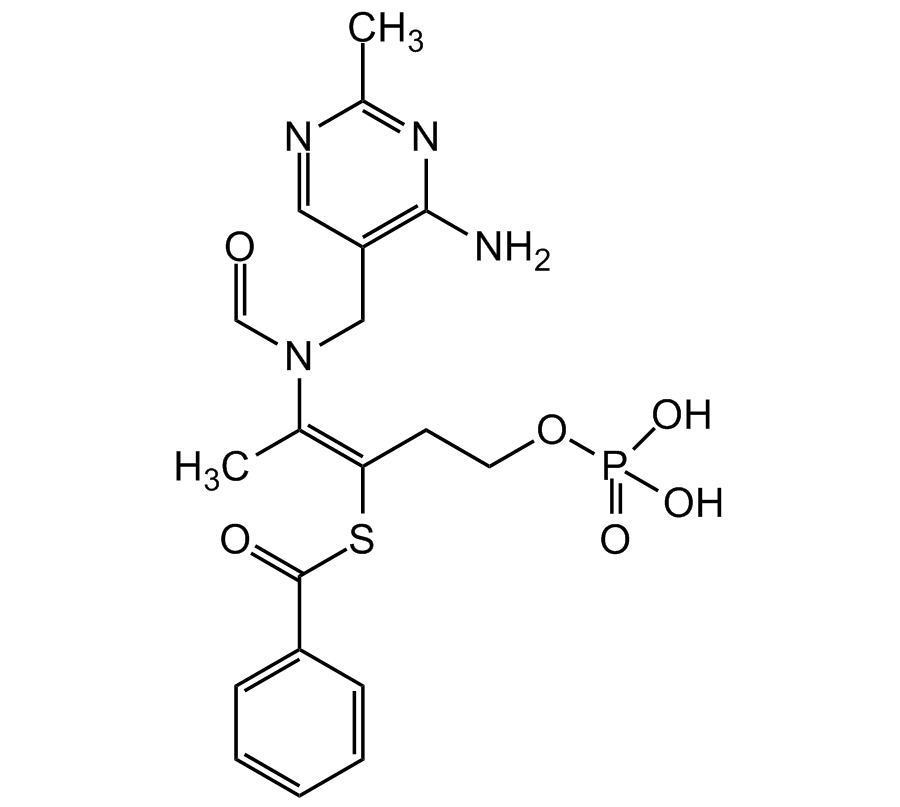
Chemical Structure
S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate [22457-89-2] [22457-89-2]
CDX-B0403
CAS Number22457-89-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight466.45
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameS-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate [22457-89-2] [22457-89-2]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number22457-89-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC19H23N4O6PS
- Molecular Weight466.45
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 22457-89-2. Formula: C19H23N4O6PS. MW: 466.45. S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate is a lipid-soluble form of vitamin B1 (thiamine). S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate facilitates the action of thiamine diphosphate, a cofactor for the enzyme transketolase. The activation of transketolase enzyme accelerates the precursors of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) towards the pentose phosphate pathway thereby reducing the production of AGEs. The reduction in AGEs subsequently decreases metabolic stress which benefits vascular complications seen in diabetes. The anti-AGE property of S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate certainly makes it effective for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy, nephropathy and retinopathy. S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate appears to have a also cardioprotective role in potentiating angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis in diabetic complications. S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate also modulates pathways such as arachidonic acid (AA), nuclear transcription Factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), protein kinase B, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) signaling pathways, which are also responsible for its anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate has been shown to be a dual inhibitory action on COX-2 and LOX-5, supressing PKC and NF-kappaB activation, preventing the downregulation of PKB/Akt during diabetic complications and enhancing cell survival, regulating GSK-3 activity through Akt (rendering its anti-AD activity) and inducing cell death through paraptosis. - S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate is a lipid-soluble form of vitamin B1 (thiamine). S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate facilitates the action of thiamine diphosphate, a cofactor for the enzyme transketolase. The activation of transketolase enzyme accelerates the precursors of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) towards the pentose phosphate pathway thereby reducing the production of AGEs. The reduction in AGEs subsequently decreases metabolic stress which benefits vascular complications seen in diabetes. The anti-AGE property of S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate certainly makes it effective for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy, nephropathy and retinopathy. S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate appears to have a also cardioprotective role in potentiating angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis in diabetic complications. S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate also modulates pathways such as arachidonic acid (AA), nuclear transcription Factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), protein kinase B, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) signaling pathways, which are also responsible for its anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate has been shown to be a dual inhibitory action on COX-2 and LOX-5, supressing PKC and NF-kappaB activation, preventing the downregulation of PKB/Akt during diabetic complications and enhancing cell survival, regulating GSK-3 activity through Akt (rendering its anti-AD activity) and inducing cell death through paraptosis.
- SMILESCC1=NC(N)=C(CN(/C(C)=C(CCOP(O)(O)=O)/SC(C2=CC=CC=C2)=O)C=O)C=N1
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Benfotiamine [22457-89-2] [22457-89-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/85/CgoaEGY7Nd6EXnzEAAAAADOoM4U114.png)