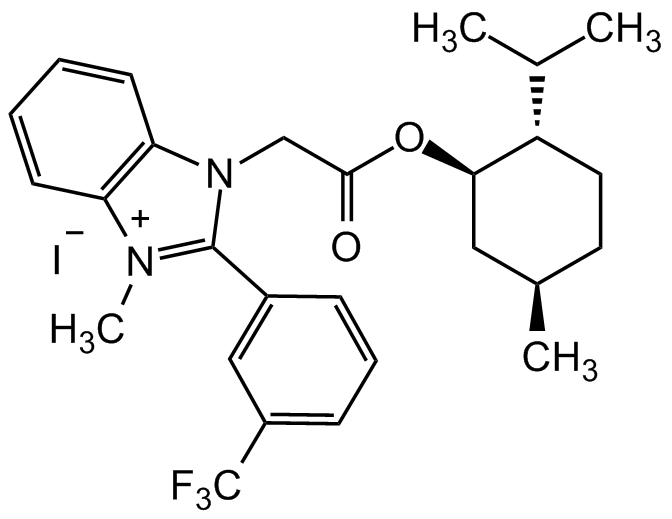
Chemical Structure
S-Gboxin iodide [2101317-21-7]
AG-CR1-3533
CAS Number2101317-21-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight473.6 . 126.9
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameS-Gboxin iodide [2101317-21-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number2101317-21-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC27H32F3N2O2 . I
- Molecular Weight473.6 . 126.9
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 2101317-21-7. Formula: C27H32F3N2O2 . I. MW: 473.6 . 126.9. Synthetic. Potent mitochondrial ATP synthase (ATPases (F0F1)) inhibitor, consequently leading to inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (F0 subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production), significantly reducing electron flow through the electron transport chain. Potent antitumor agent that inhibits oxidative phosphorylation and consequently growth and proliferation of mouse and human glioblastoma (GBM) with an IC50 of 470nM. Shown to rapidly and irreversibly compromise oxygen consumption in glioblastoma cells. This functional Gboxin analog has excellent metabolic stability, enhanced plasma stability and pharmacokinetic properties, and is suitable for in vivo studies. Gboxin-resistant cells require a functional mitochondrial permeability transition pore that regulates pH and thus impedes the accumulation of Gboxin in the mitochondrial matrix. Administration of a metabolically stable Gboxin analog inhibits glioblastoma allografts and patient-derived xenografts. Gboxin toxicity extends to established human cancer cell lines of diverse organ origin and shows that the increased proton gradient and pH in cancer cell mitochondria is a mode of action that can be targeted in the development of antitumor reagents. - Potent mitochondrial ATP synthase (ATPases (F0F1)) inhibitor, consequently leading to inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (F0 subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production), significantly reducing electron flow through the electron transport chain. Potent antitumor agent that inhibits oxidative phosphorylation and consequently growth and proliferation of mouse and human glioblastoma (GBM) with an IC50 of 470nM. Shown to rapidly and irreversibly compromise oxygen consumption in glioblastoma cells. This functional Gboxin analog has excellent metabolic stability, enhanced plasma stability and pharmacokinetic properties, and is suitable for in vivo studies. Gboxin-resistant cells require a functional mitochondrial permeability transition pore that regulates pH and thus impedes the accumulation of Gboxin in the mitochondrial matrix. Administration of a metabolically stable Gboxin analog inhibits glioblastoma allografts and patient-derived xenografts. Gboxin toxicity extends to established human cancer cell lines of diverse organ origin and shows that the increased proton gradient and pH in cancer cell mitochondria is a mode of action that can be targeted in the development of antitumor reagents.
- SMILESCC(C)[C@@H]1CC[C@@H](C)C[C@H]1OC(CN2C(C=CC=C3)=C3[N+](C)=C2C4=CC(C (F)(F)F)=CC=C4)=O.[I-]
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![S-Gboxin [2101317-21-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/A8/CgoaEGayQdmEcjWSAAAAAIlLWpo719.png)