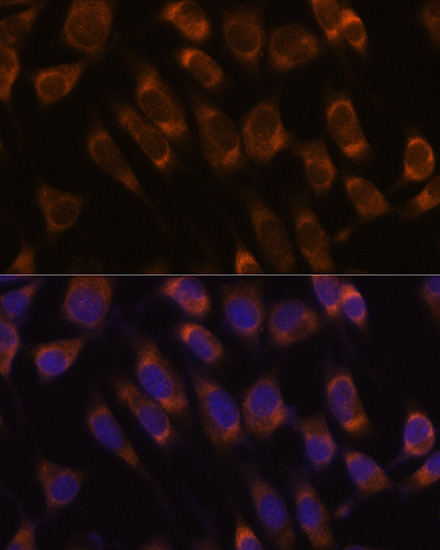
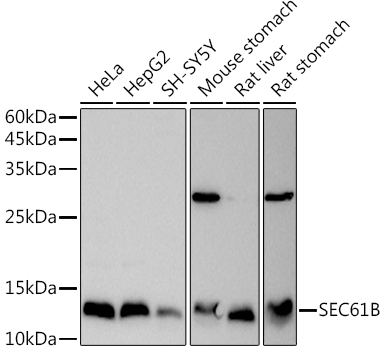
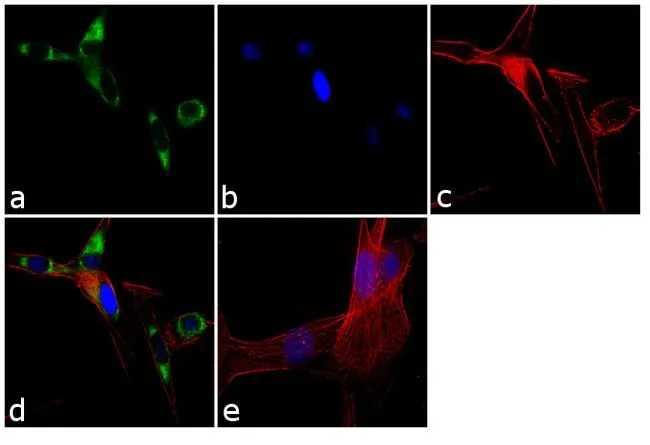
SEC61B antibody
GTX129852
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetSEC61B
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSEC61B antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IP: 1:100-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.77 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID10952
- Target nameSEC61B
- Target descriptionSEC61 translocon subunit beta
- Target synonymsprotein transport protein Sec61 subunit beta, SEC61 translocon beta subunit, Sec61 beta subunit, Sec61 complex, beta subunit, protein translocation complex beta, protein transport protein SEC61 beta subunit
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP60468
- Protein NameProtein transport protein Sec61 subunit beta
- Scientific DescriptionThe Sec61 complex is the central component of the protein translocation apparatus of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Oligomers of the Sec61 complex form a transmembrane channel where proteins are translocated across and integrated into the ER membrane. This complex consists of three membrane proteins- alpha, beta, and gamma. This gene encodes the beta-subunit protein. The Sec61 subunits are also observed in the post-ER compartment, suggesting that these proteins can escape the ER and recycle back. There is evidence for multiple polyadenylated sites for this transcript. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Chen MK, Du Y, Sun L, et al. H(2)O(2) induces nuclear transport of the receptor tyrosine kinase c-MET in breast cancer cells via a membrane-bound retrograde trafficking mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2019,294(21):8516-8528. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005953Read this paper