Serum Amyloid A antibody [291]
GTX18713
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSAA1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSerum Amyloid A antibody [291]
- Delivery Days Customer9
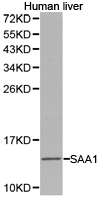
- Application Supplier NoteFor ELISA: Use at an assay dependent dilution. For WB: Use at a concentration of 0.1 - 0.5 microg/ml. Detects a band of approximately 12 kDa (predicted molecular weight: 14 kDa). Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID291
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6288
- Target nameSAA1
- Target descriptionserum amyloid A1
- Target synonymsPIG4, SAA, SAA2, TP53I4, serum amyloid A-1 protein, serum amyloid A protein, tumor protein p53 inducible protein 4
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Scientific DescriptionThe serum amyloid A family comprises a number of differentially expressed apolipoproteins, acute-phase SAA1 and SAA2, the former being the major component in plasma and constitutive SAAs. Although the liver is the primary site of synthesis of both SAA types extrahepatic production has been reported. The in vivo concentrations increase by as much as 1000 fold during inflammation. Several studies have expressed its importance in the diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases. Pathological SAA values are often detected in association with normal CRP concentrations; SAA rises earlier and more sharply than CRP. Recently, a broader view of SAA expression and function has been emerging. Expression studies show production of SAA proteins in histologically normal, atherosclerotic, Alzheimer, inflammatory, and tumour tissues. SAA has been found to have binding sites for high density lipoproteins, calcium, laminin, and heparin/heparin sulphate. Also adhesion motifs were identified and new functions affecting cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and aggregation were discovered. These findings emphasize the importance of SAA in various physiological and pathological processes including inflammation, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, AA-amyloidosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and neoplasia. SAA has also a number of immunomodulatory roles, it can induce chemotaxis and adhesion molecule expression, has cytokine-like properties and can promote the upregulation of metalloproteinases. It enhances the binding of high density lipoprotein to macrophages and thus helps in the delivery of lipids to sites of injury for use in tissue repair, it is thus thought to be an integral part of the disease process.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203