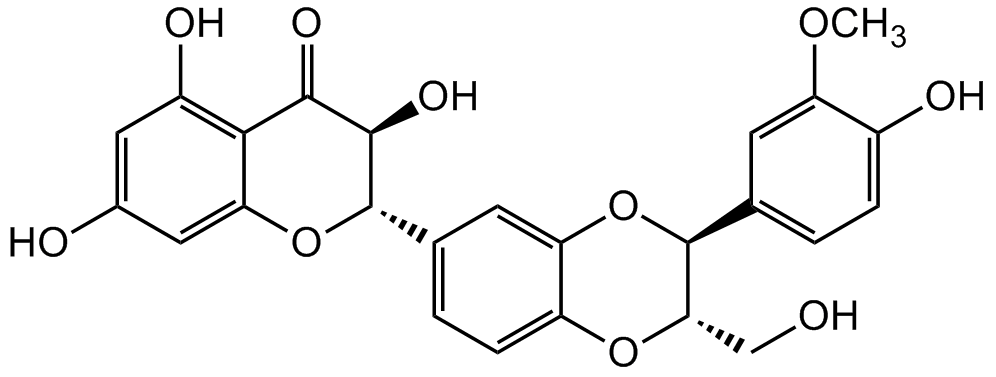
Chemical Structure
Silibinin [22888-70-6] [22888-70-6]
CDX-S0276
CAS Number22888-70-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight482.44
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameSilibinin [22888-70-6] [22888-70-6]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number22888-70-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC25H22O10
- Molecular Weight482.44
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 22888-70-6. Formula: C25H22O10. MW: 482.44. Silibinin is a naturally occurring flavanone from Silybum marianum (milk thistle plant) and the main component (active principle) of the Silymarin extract. Silibinin has shown pleiotropic biological properties, including potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, antiviral, antimicrobial and immunosuppressive activities. Silibinin demonstrates promising anticancer effects in vitro and in vivo. The molecular mechanisms of silibinin-mediated antiproliferative effects are mainly via receptor tyrosine kinases, androgen receptor, STATs, NF-kappaB, cell cycle arrest and apoptotis/autophagy inducing signaling pathways in various cancer cells. Silibinin was reported to improve glycemic homeostasis by improving the activity of pancreatic beta-cells, increasing insulin sensitivity of liver and muscle cells and decreasing lipid deposition in adipocytes. Next to modulating the NFkappa signaling pathway, Sibilin also inhibits NLRP1/NLRP3 inflammasomes signaling pathways. It modulates many molecular changes caused by xenobiotics and ultraviolet radiation to protect the skin and is used in cosmeceutical preparations. - Silibinin is a naturally occurring flavanone from Silybum marianum (milk thistle plant) and the main component (active principle) of the Silymarin extract. Silibinin has shown pleiotropic biological properties, including potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, antiviral, antimicrobial and immunosuppressive activities. Silibinin demonstrates promising anticancer effects in vitro and in vivo. The molecular mechanisms of silibinin-mediated antiproliferative effects are mainly via receptor tyrosine kinases, androgen receptor, STATs, NF-kappaB, cell cycle arrest and apoptotis/autophagy inducing signaling pathways in various cancer cells. Silibinin was reported to improve glycemic homeostasis by improving the activity of pancreatic beta-cells, increasing insulin sensitivity of liver and muscle cells and decreasing lipid deposition in adipocytes. Next to modulating the NFkappa signaling pathway, Sibilin also inhibits NLRP1/NLRP3 inflammasomes signaling pathways. It modulates many molecular changes caused by xenobiotics and ultraviolet radiation to protect the skin and is used in cosmeceutical preparations.
- SMILESOC1=C2C(O[C@@H](C3=CC=C(O[C@@H](CO)[C@H](C4=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C4)O5)C5=C3)[C@H](O)C2=O)=CC(O)=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Silibinin [22888-70-6] [22888-70-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/03/14/CgoaEGY7Rk6EW2zHAAAAACRHjZ8697.png)