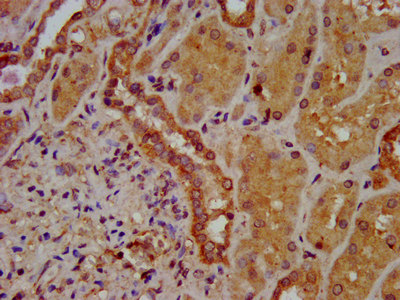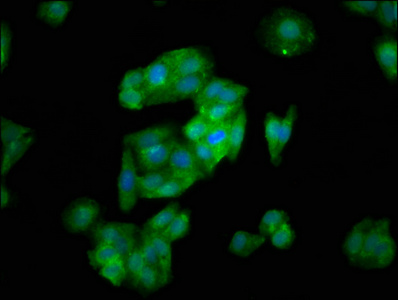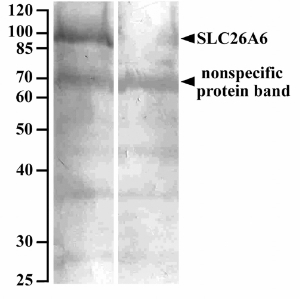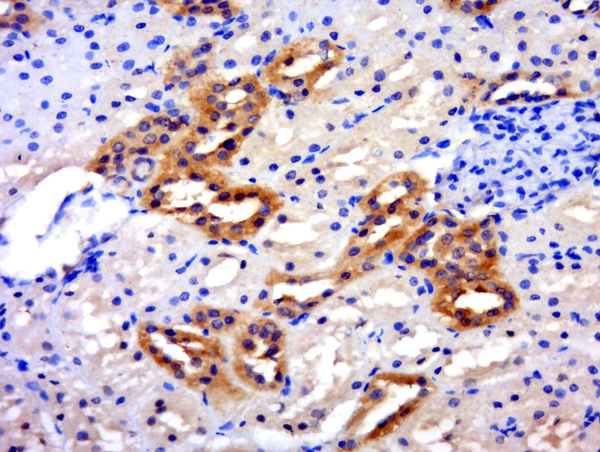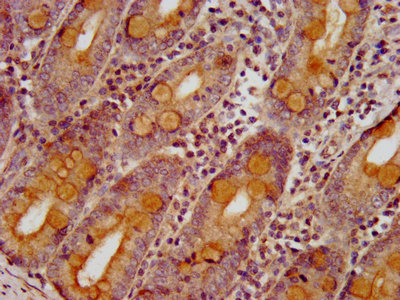
IHC image of CSB-PA861164LA01HU diluted at 1:400 and staining in paraffin-embedded human small intestine tissue performed on a Leica BondTM system. After dewaxing and hydration, antigen retrieval was mediated by high pressure in a citrate buffer (pH 6.0). Section was blocked with 10% normal goat serum 30min at RT. Then primary antibody (1% BSA) was incubated at 4°C overnight. The primary is detected by a biotinylated secondary antibody and visualized using an HRP conjugated SP system.
SLC26A6 Antibody
CSB-PA861164LA01HU
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSLC26A6
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameSLC26A6 Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID65010
- Target nameSLC26A6
- Target descriptionsolute carrier family 26 member 6
- Target synonymssolute carrier family 26 member 6, anion exchange transporter, anion transporter 1, pendrin L1, solute carrier family 26 (anion exchanger), member 6, sulfate anion transporter
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9BXS9
- Protein NameSolute carrier family 26 member 6
- Scientific DescriptionApical membrane anion-exchanger with wide epithelial distribution that plays a role as a component of the pH buffering system for maintaining acid-base homeostasis. Acts as a versatile DIDS-sensitive inorganic and organic anion transporter that mediates the uptake of monovalent anions like chloride, bicarbonate, formate and hydroxyl ion and divalent anions like sulfate and oxalate. Function in multiple exchange modes involving pairs of these anions, which include chloride-bicarbonate, chloride-oxalate, oxalate-formate, oxalate-sulfate and chloride-formate exchange. Apical membrane chloride-bicarbonate exchanger that mediates luminal chloride absorption and bicarbonate secretion by the small intestinal brush border membrane and contributes to intracellular pH regulation in the duodenal upper villous epithelium during proton-coupled peptide absorption, possibly by providing a bicarbonate import pathway. Mediates also intestinal chloride absorption and oxalate secretion, thereby preventing hyperoxaluria and calcium oxalate urolithiasis. Transepithelial oxalate secretion, chloride-formate, chloride-oxalate and chloride-bicarbonate transport activities in the duodenum are inhibited by PKC activation in a calcium-independent manner. The apical membrane chloride-bicarbonate exchanger provides also a major route for fluid and bicarbonate secretion into the proximal tubules of the kidney as well as into the proximal part of the interlobular pancreatic ductal tree, where it mediates electrogenic chloride-bicarbonate exchange with a chloride-bicarbonate stoichiometry of 1:2, and hence will dilute and alkalinize protein-rich acinar secretion. Mediates also the transcellular sulfate absorption and oxalate secretion across the apical membrane in the duodenum and the formate ion efflux at the apical brush border of cells in the proximal tubules of kidney. Plays a role in sperm capacitation by increasing intracellular pH.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161