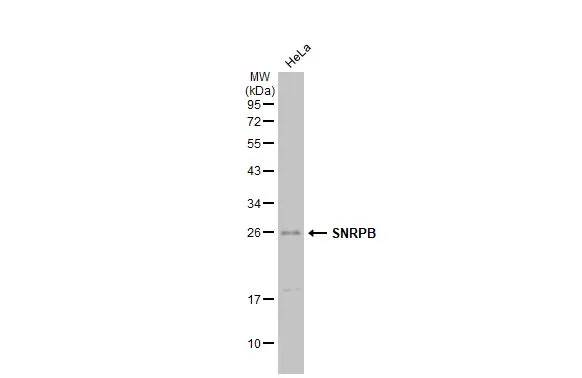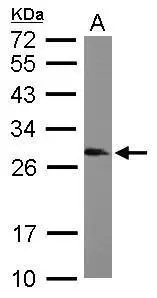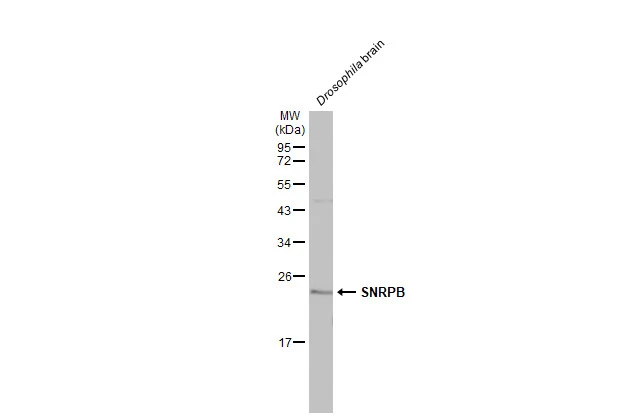
Drosophila tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with SNRPB antibody (GTX101883) diluted at 1:2000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.
SNRPB antibody
GTX101883
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityDrosophila, Human
TargetSNRPB
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSNRPB antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.38 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6628
- Target nameSNRPB
- Target descriptionsmall nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptides B and B1
- Target synonymsCCMS, COD, SNRPB1, Sm-B/B', SmB/B', SmB/SmB', snRNP-B, small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated proteins B and B', B polypeptide of Sm protein, Sm protein B/B', sm-B/Sm-B', small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide B, small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptides B and B'
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP14678
- Protein NameSmall nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated proteins B and B'
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is one of several nuclear proteins that are found in common among U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 small ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs). These snRNPs are involved in pre-mRNA splicing, and the encoded protein may also play a role in pre-mRNA splicing or snRNP structure. Autoantibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus frequently recognize epitopes on the encoded protein. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms (B and B) have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityDrosophila, Human
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

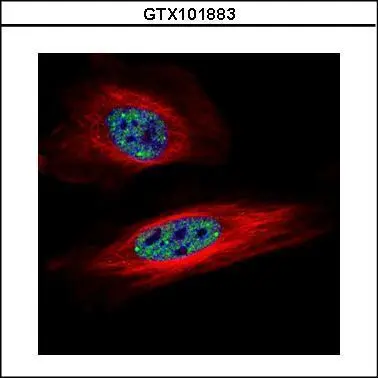
![SNRPB antibody detects SNRPB protein at cytoplasm and nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: SNRPB stained by SNRPB antibody (GTX101883) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Scale bar= 10μm. SNRPB antibody detects SNRPB protein at cytoplasm and nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: SNRPB stained by SNRPB antibody (GTX101883) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Scale bar= 10μm.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101883/GTX101883_44552_20220401_ICC_IF_w_23060100_911.webp)