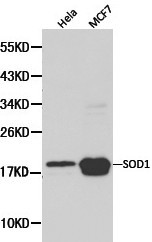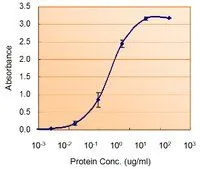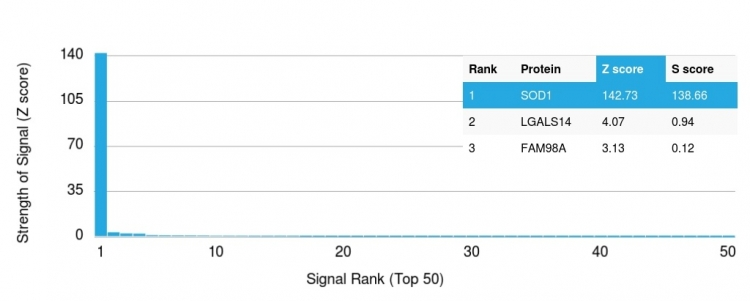
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using Superoxide Dismutase 1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SOD1/2089). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SD’s) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SD’s) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a Monoclonal Antibody to its intended target. A Monoclonal Antibody is considered to specific to its intended target if the Monoclonal Antibody has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a Monoclonal Antibody binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that Monoclonal Antibody to protein X is equal to 29.
SOD1 antibody [SOD1/2089]
GTX18134
ApplicationsELISA, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSOD1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSOD1 antibody [SOD1/2089]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteELISA: 1-5microg/ml (for coating). *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsELISA, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDSOD1/2089
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6647
- Target nameSOD1
- Target descriptionsuperoxide dismutase 1
- Target synonymsALS, ALS1, HEL-S-44, IPOA, SOD, STAHP, hSod1, homodimer, superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn], Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase, SOD, soluble, epididymis secretory protein Li 44, indophenoloxidase A, superoxide dismutase 1, soluble, superoxide dismutase, cystolic
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP00441
- Protein NameSuperoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn]
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene binds copper and zinc ions and is one of two isozymes responsible for destroying free superoxide radicals in the body. The encoded isozyme is a soluble cytoplasmic protein, acting as a homodimer to convert naturally-occuring but harmful superoxide radicals to molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. The other isozyme is a mitochondrial protein. Mutations in this gene have been implicated as causes of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Rare transcript variants have been reported for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203