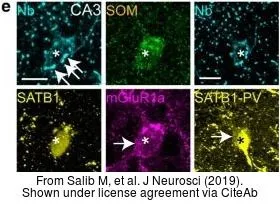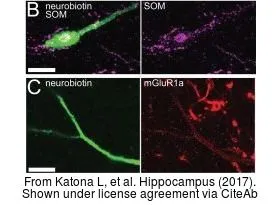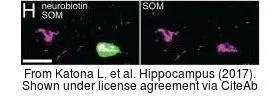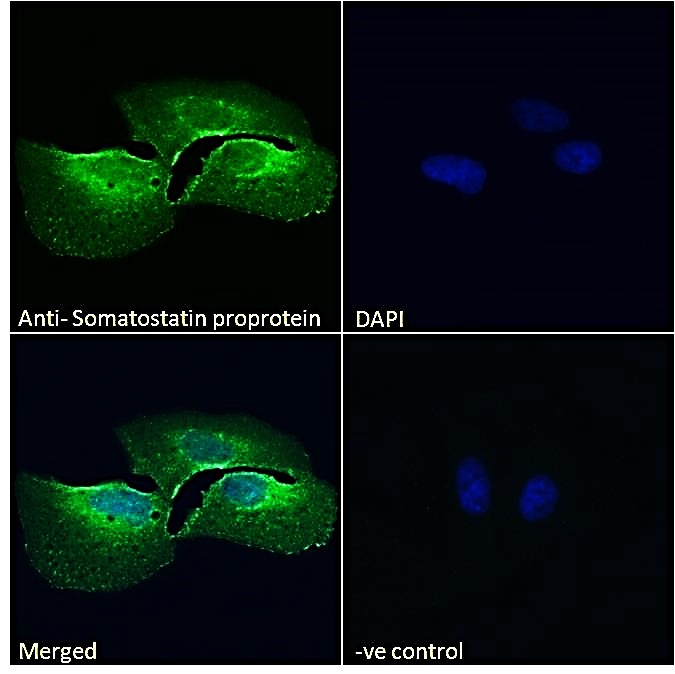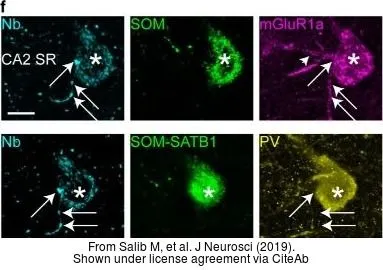
The data was published in the journal J Neurosci in 2019.
Somatostatin antibody [SOM-018]
GTX71935
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetSST
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSomatostatin antibody [SOM-018]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteRecommended Starting Dilutions:For ICC/IF: Use at a dilution of 1:25-1:100For IHC-Fr: Use at a dilution of 1:25-1:100For IHC-P: Use at a dilution of 1:25-1:100Not yet tested in other applications. Optimal dilutions should be determined experimentally by the researcher.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDSOM-018
- Concentration0.14 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6750
- Target nameSST
- Target descriptionsomatostatin
- Target synonymsSMST, SST1, somatostatin, growth hormone release-inhibiting factor, prepro-somatostatin, somatostatin-14, somatostatin-28
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP61278
- Protein NameSomatostatin
- Scientific DescriptionThe hormone somatostatin has active 14 aa and 28 aa forms that are produced by alternate cleavage of the single preproprotein encoded by this gene. Somatostatin is expressed throughout the body and inhibits the release of numerous secondary hormones by binding to high-affinity G-protein-coupled somatostatin receptors. This hormone is an important regulator of the endocrine system through its interactions with pituitary growth hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, and most hormones of the gastrointestinal tract. Somatostatin also affects rates of neurotransmission in the central nervous system and proliferation of both normal and tumorigenic cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161