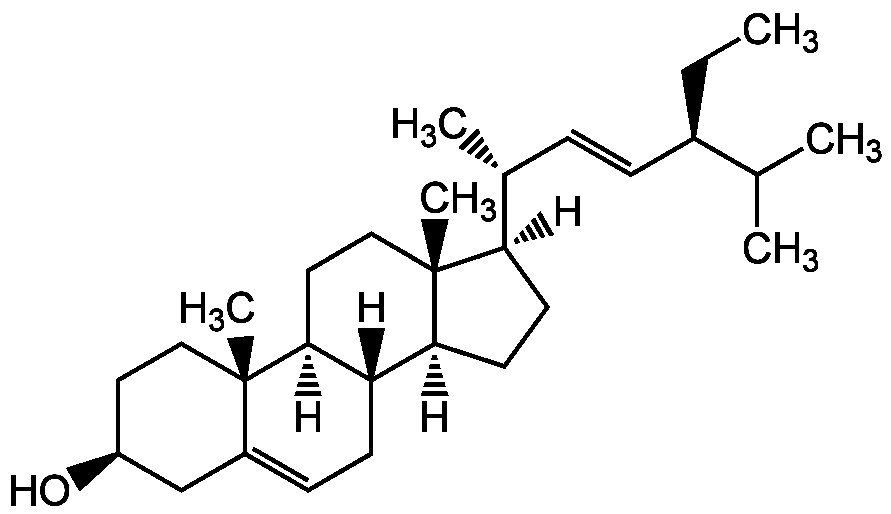
Chemical Structure
Stigmasterol [83-48-7] [83-48-7]
AG-CN2-0412
CAS Number83-48-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight412.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameStigmasterol [83-48-7] [83-48-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number83-48-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC29H48O
- Molecular Weight412.7
- Scientific DescriptionAnti-hypercholestrolemic compound [1, 7]. Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects [2, 4]. Anticancer compound. Chemopreventive [3, 12, 13]. Cytostatic. Cell growth inhibitor [5]. Antimutagenic [6]. Potent in vitro antagonist of FXR (farnesoid X receptor) [8]. DNA polymerase beta inhibitor [9]. Potent antioxidant, hypoglycemic and thyroid inhibiting agent [10]. Anti-osteoarthritic. Decreases the expression of matrix metalloproteinases [11]. Neuroprotective [15]. Is used as a precursor for synthetic progesterone and vitamin D3 and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of androgens, estrogens and corticoids [14]. - Chemical. CAS: 83-48-7. Formula: C29H48O. MW: 412.7. Synthetic. Originally isolated from various plants and marine organisms. Anti-hypercholestrolemic compound. Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects. Anticancer compound. Chemopreventive. Cytostatic. Cell growth inhibitor. Antimutagenic. Potent in vitro antagonist of FXR (farnesoid X receptor). DNA polymerase beta inhibitor. Potent antioxidant, hypoglycemic and thyroid inhibiting agent. Anti-osteoarthritic. Decreases the expression of matrix metalloproteinases. Neuroprotective. Is used as a precursor for synthetic progesterone and vitamin D3 and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of androgens, estrogens and corticoids.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)\C=C\[C@@H](CC)C(C)C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

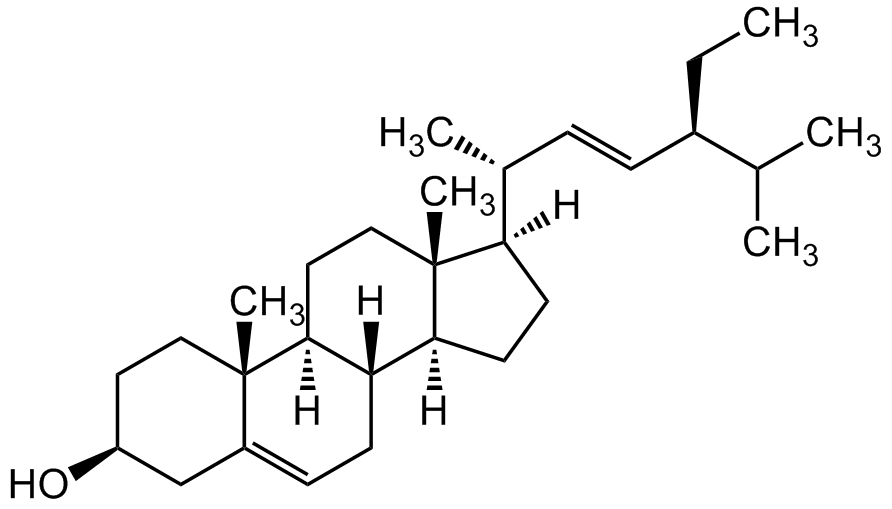
![Stigmasterol [83-48-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/34/D5/CgoaEWayCgqESHWfAAAAAOnv9VU811.png)