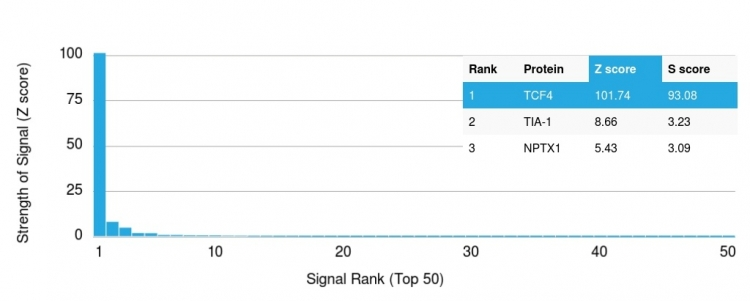
Analysis of Protein Array containing more than 19,000 full-length human proteins using TCF4 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (TCF4/1705). Z- and S- Score: The Z-score represents the strength of a signal that a monoclonal antibody produces when binding to a particular protein on the HuProtTM array. Z-scores are described in units of standard deviations (SDs) above the mean value of all signals generated on that array. If targets on HuProtTM are arranged in descending order of the Z-score, the S-score is the difference (also in units of SDs) between the Z-score. S-score therefore represents the relative target specificity of a Monoclonal Antibody to its intended target. A Monoclonal Antibody is considered to specific to its intended target if the Monoclonal Antibody has an S-score of at least 2.5. For example, if a Monoclonal Antibody binds to protein X with a Z-score of 43 and to protein Y with a Z-score of 14, then the S-score for the binding of that Monoclonal Antibody to protein X is equal to 29.
TCF4 antibody [TCF4/1705]
GTX17912
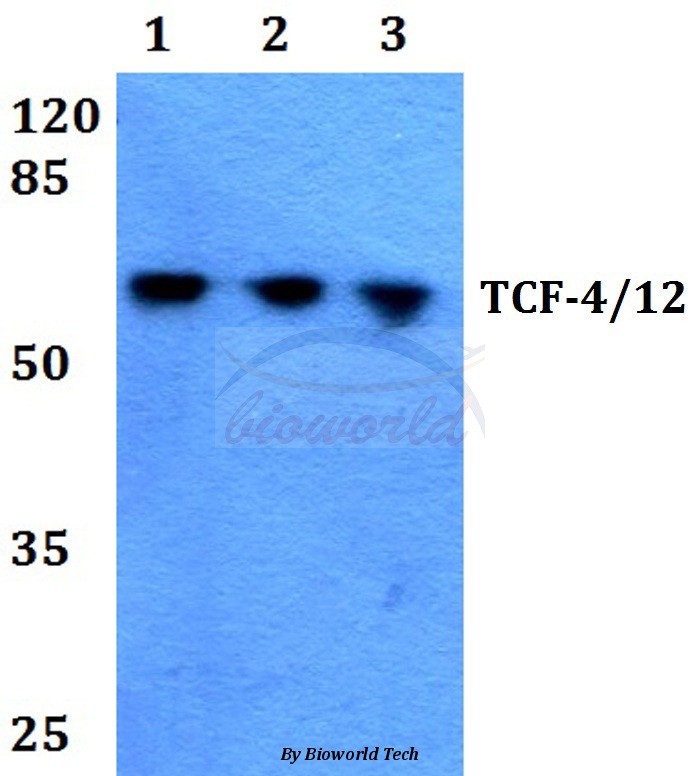
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTCF4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTCF4 antibody [TCF4/1705]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1-2microg/ml. ELISA: 2-4microg/ml (for coating). *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDTCF4/1705
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6925
- Target nameTCF4
- Target descriptiontranscription factor 4
- Target synonymsCDG2T, E2-2, FCD2, FECD3, ITF-2, ITF2, PTHS, SEF-2, SEF2, SEF2-1, SEF2-1A, SEF2-1B, SEF2-1D, TCF-4, bHLHb19, transcription factor 4, SL3-3 enhancer factor 2, class B basic helix-loop-helix protein 19, immunoglobulin transcription factor 2
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP15884
- Protein NameTranscription factor 4
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes transcription factor 4, a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. The encoded protein recognizes an Ephrussi-box (E-box) binding site (CANNTG) - a motif first identified in immunoglobulin enhancers. This gene is broadly expressed, and may play an important role in nervous system development. Defects in this gene are a cause of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. In addition, an intronic CTG repeat normally numbering 10-37 repeat units can expand to >50 repeat units and cause Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different proteins have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Hsu YH, Pintacuda G, Liu R, et al. Using brain cell-type-specific protein interactomes to interpret neurodevelopmental genetic signals in schizophrenia. iScience. 2023,26(5):106701. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106701Read this paper
- Wen N, Bian L, Gong J, et al. Overexpression of cell-cycle related and expression-elevated protein in tumor (CREPT) in malignant cervical cancer. J Int Med Res. 2020,48(1):300060519895089. doi: 10.1177/0300060519895089Read this paper

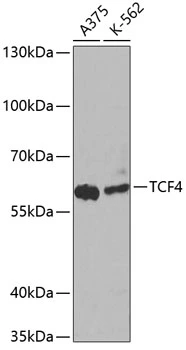
![WB analysis of (1) HeLa and (2) HepG2 cell lysates using GTX17912 TCF4 antibody [TCF4/1705]. WB analysis of (1) HeLa and (2) HepG2 cell lysates using GTX17912 TCF4 antibody [TCF4/1705].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX17912/GTX17912_20200115_WB_1_w_23060620_960.webp)