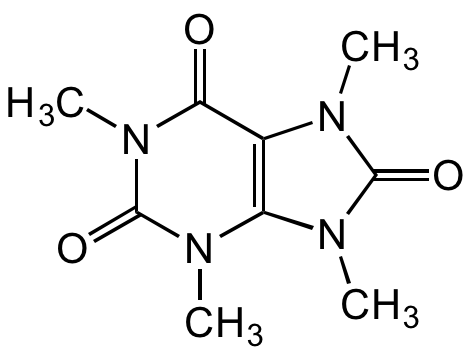
Chemical Structure
Theacrine [2309-49-1]
AG-CN2-0466
CAS Number2309-49-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight224.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameTheacrine [2309-49-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number2309-49-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC9H12N4O3
- Molecular Weight224.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 2309-49-1. Formula: C9H12N4O3. MW: 224.2. Synthetic. Originally isolated from Theobroma grandiflorum. Purine alkaloid related to caffeine. Potent antioxidant. Not through direct scavenging of ROS but strengthen antioxidant systems in vivo. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive compound. Suggested to have adenosine receptor agonistic activity and also acting on dopamine receptors. Shown to have potent sedative and hypnotic properties. Ameliorated learning and memory impairments caused by central fatigue. Shown to inhibit cAMP-specific PDE4 and cGMP-specific PDE5 activity in vivo and in vitro. Increased glucose level, decreased lactic acid concentration, reduced LDH activity and elevated the expressions of both GLUT1/3 in restraint-stressed mice. Can increase the solubility of aromatic systems in water. - Purine alkaloid related to caffeine. Potent antioxidant. Not through direct scavenging of ROS but strengthen antioxidant systems in vivo. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive compound. Suggested to have adenosine receptor agonistic activity and also acting on dopamine receptors. Shown to have potent sedative and hypnotic properties. Ameliorated learning and memory impairments caused by central fatigue. Shown to inhibit cAMP-specific PDE4 and cGMP-specific PDE5 activity in vivo and in vitro. Increased glucose level, decreased lactic acid concentration, reduced LDH activity and elevated the expressions of both GLUT1/3 in restraint-stressed mice. Can increase the solubility of aromatic systems in water.
- SMILESCN1C(=O)N(C)C2=C1N(C)C(=O)N(C)C2=O
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200

