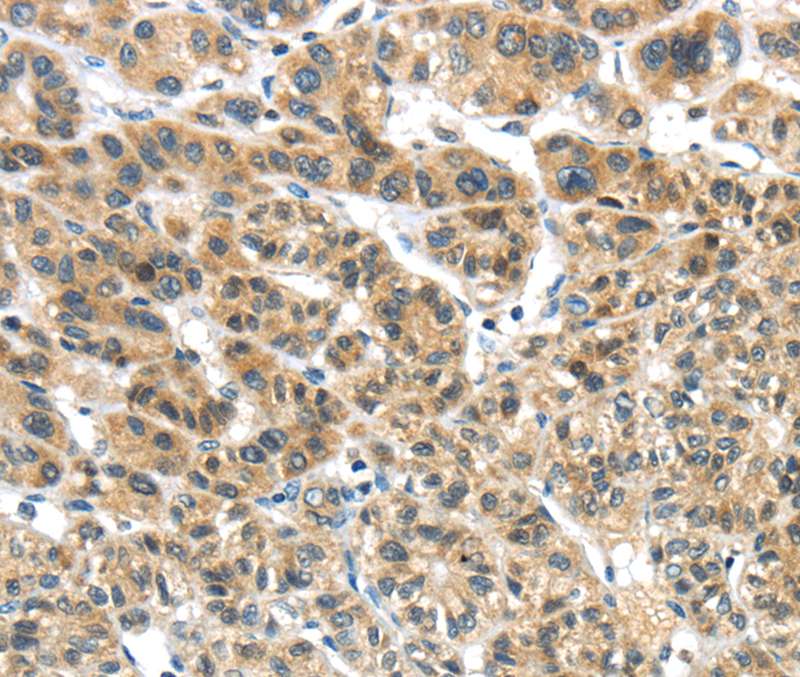
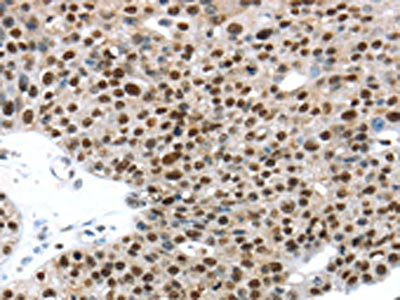
![TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] detects TKTL1 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: TKTL1 protein stained by TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] (GTX109459) diluted at 1:500. Red: Phalloidin, a cytoskeleton marker, diluted at 1:100. Scale bar = 10 μm. TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] detects TKTL1 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: TKTL1 protein stained by TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] (GTX109459) diluted at 1:500. Red: Phalloidin, a cytoskeleton marker, diluted at 1:100. Scale bar = 10 μm.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX109459/GTX109459_42907_20170802_IFA_w_23060500_480.webp)
TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] detects TKTL1 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: TKTL1 protein stained by TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] (GTX109459) diluted at 1:500. Red: Phalloidin, a cytoskeleton marker, diluted at 1:100. Scale bar = 10 μm.
TKTL1 antibody [N1C1]
GTX109459
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTKTL1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTKTL1 antibody [N1C1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.98 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID8277
- Target nameTKTL1
- Target descriptiontransketolase like 1
- Target synonymsTKR, TKT2, transketolase-like protein 1, TK 2, transketolase-2, transketolase-related protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP51854
- Protein NameTransketolase-like protein 1
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] (GTX109459) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with TKTL1 antibody [N1C1] (GTX109459) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX109459/GTX109459_43712_20240705_WB_24070822_403.webp)