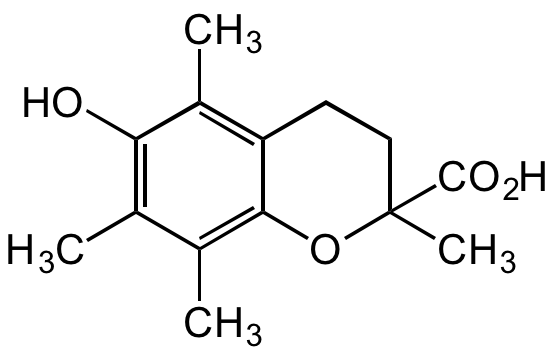
Chemical Structure
Trolox [53188-07-1] [53188-07-1]
AG-CR1-3639
CAS Number53188-07-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight250.3
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameTrolox [53188-07-1] [53188-07-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number53188-07-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC14H18O4
- Molecular Weight250.3
- Scientific DescriptionCell permeable and water soluble derivative of vitamin E. Potent antioxidant. Efficiently prevents formation of different reactive oxygen species, such as singlet oxygen (1O2), superoxide anion (O2-) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Commonly used as a standard or positive control in different antioxidant assays, such as ABTS decolorization and FRAP assays, measuring Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC). TEAC assays are used to measure antioxidant capacity of foods, beverages and supplements. Used in biological or biochemical applications to reduce oxidative stress or damage, such as inhibiting peroxynitrite mediated tyrosine nitration and mitochondrial proton permeability. Cytoprotective with low cytotoxicity for different cell lines. Shown to have anticancer activity and to be effective as adjunctive agent in cancer treatments. Used to reduce fluorophore bleaching as well as the fluorophore blinking during the observation of fluorescent labels. Freezing extender supplement in cryopreservation media to improve the quality of cryopreserved human sperm. - Chemical. CAS: 53188-07-1. Formula: C14H18O4. MW: 250.3. Cell permeable and water soluble derivative of vitamin E. Potent antioxidant. Efficiently prevents formation of different reactive oxygen species, such as singlet oxygen (1O2), superoxide anion (O2-) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Commonly used as a standard or positive control in different antioxidant assays, such as ABTS decolorization and FRAP assays, measuring Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC). TEAC assays are used to measure antioxidant capacity of foods, beverages and supplements. Used in biological or biochemical applications to reduce oxidative stress or damage, such as inhibiting peroxynitrite mediated tyrosine nitration and mitochondrial proton permeability. Cytoprotective with low cytotoxicity for different cell lines. Shown to have anticancer activity and to be effective as adjunctive agent in cancer treatments. Used to reduce fluorophore bleaching as well as the fluorophore blinking during the observation of fluorescent labels. Freezing extender supplement in cryopreservation media to improve the quality of cryopreserved human sperm.
- SMILESCC1=C2C(OC(C)(C(O)=O)CC2)=C(C)C(C)=C1O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200



![Trolox [53188-07-1] [53188-07-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/03/8A/CgoaEWY7TzGEG8cAAAAAALn1GxA065.png)