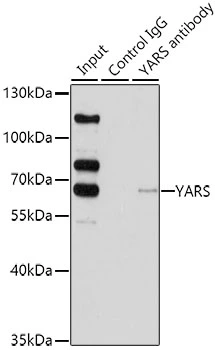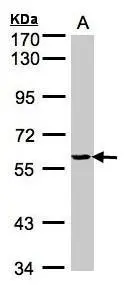
Sample(30 ug whole cell lysate) A:H1299 7.5% SDS PAGE GTX101492 diluted at 1:1000
Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase antibody
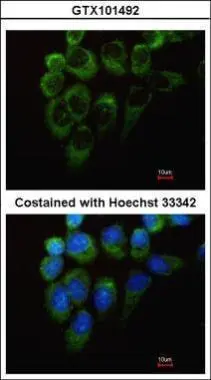
GTX101492
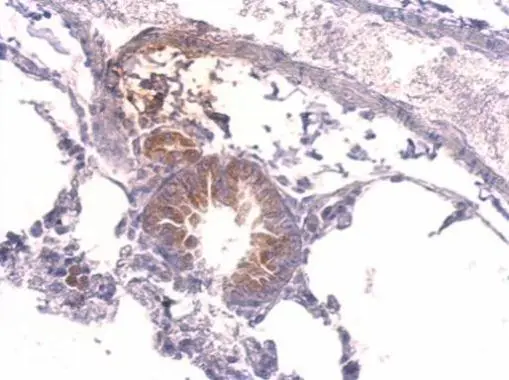
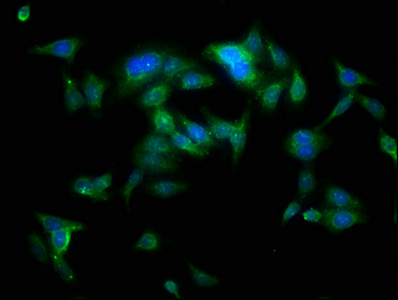
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetYARS1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTyrosyl tRNA synthetase antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.25 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID8565
- Target nameYARS1
- Target descriptiontyrosyl-tRNA synthetase 1
- Target synonymsCMTDIC, IMNEPD2, TYRRS, YARS, YRS, YTS, tyrosine--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic, tyrosine tRNA ligase 1, cytoplasmic, tyrosyl--tRNA ligase, tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, cytoplasmic
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP54577
- Protein NameTyrosine--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic
- Scientific DescriptionAminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase belongs to the class I tRNA synthetase family. Cytokine activities have also been observed for the human tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, after it is split into two parts, an N-terminal fragment that harbors the catalytic site and a C-terminal fragment found only in the mammalian enzyme. The N-terminal fragment is an interleukin-8-like cytokine, whereas the released C-terminal fragment is an EMAP II-like cytokine. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161