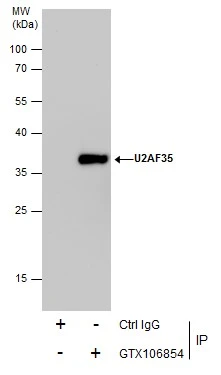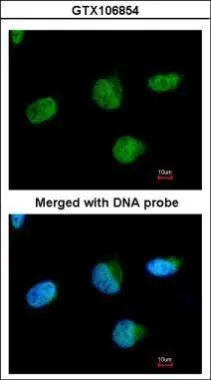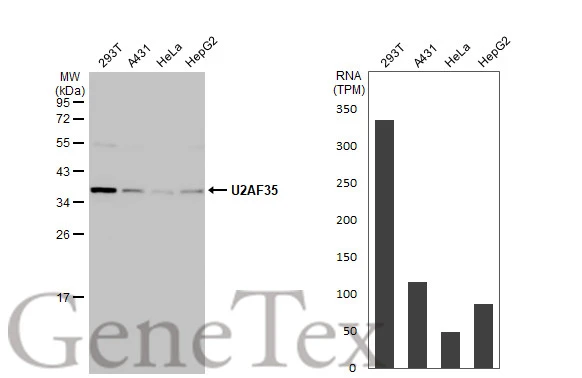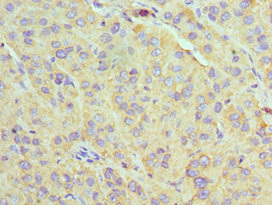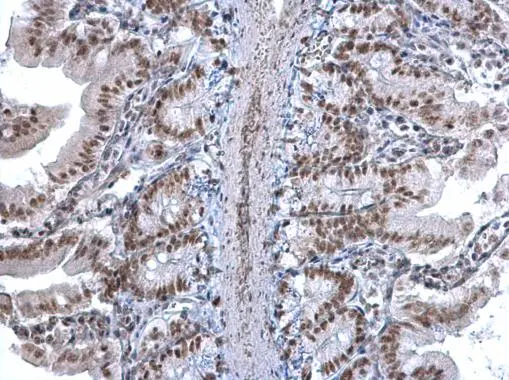
U2AF35 antibody detects U2AF35 protein at nucleus on mouse intestine by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse intestine. U2AF35 antibody (GTX106854) diluted at 1:1000.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min
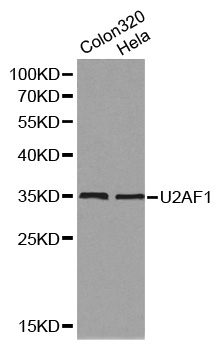
U2AF35 antibody
GTX106854
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetU2AF1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameU2AF35 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.25 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7307
- Target nameU2AF1
- Target descriptionU2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 1
- Target synonymsFP793, RN, RNU2AF1, U2AF35, U2AFBP, splicing factor U2AF 35 kDa subunit, U2 small nuclear RNA auxillary factor 1, U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxillary factor, 35-KD subunit, U2 snRNP auxiliary factor small subunit, U2(RNU2) small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor binding protein, splicing factor U2AF 35kDa subunit
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP0DN76
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene belongs to the splicing factor SR family of genes. U2 auxiliary factor, comprising a large and a small subunit, is a non-snRNP protein required for the binding of U2 snRNP to the pre-mRNA branch site. This gene encodes the small subunit which plays a critical role in both constitutive and enhancer-dependent RNA splicing by directly mediating interactions between the large subunit and proteins bound to the enhancers. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161