Ubiquitin-AMC (human) (rec.) (untagged)
SBB-PS0043
Protein IDP0CG47
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierSouth Bay Bio
- Product NameUbiquitin-AMC (human) (rec.) (untagged)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateAMCA
- Estimated Purity>99%
- Gene ID7314
- Target nameUBB
- Target descriptionubiquitin B
- Target synonymsHEL-S-50, polyubiquitin-B, epididymis secretory protein Li 50, polyubiquitin B
- Protein IDP0CG47
- Protein NamePolyubiquitin-B
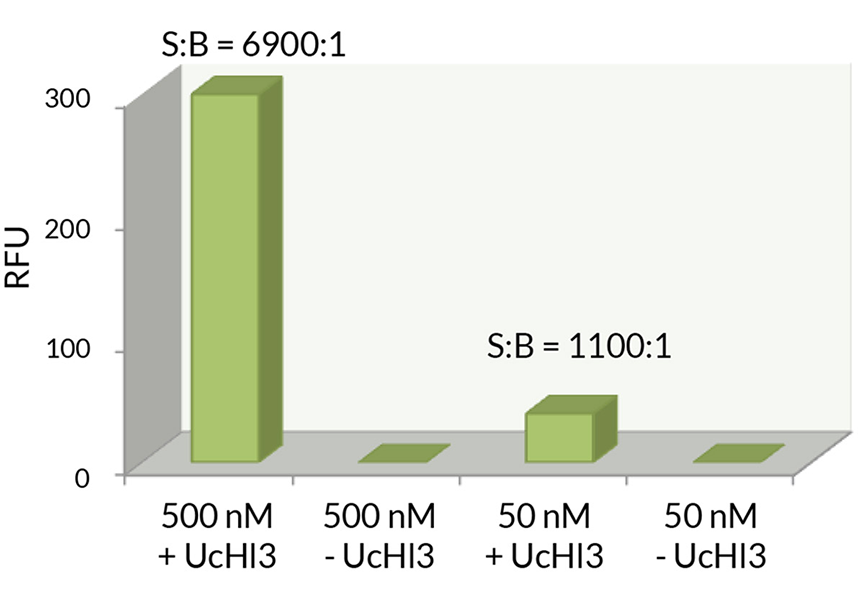
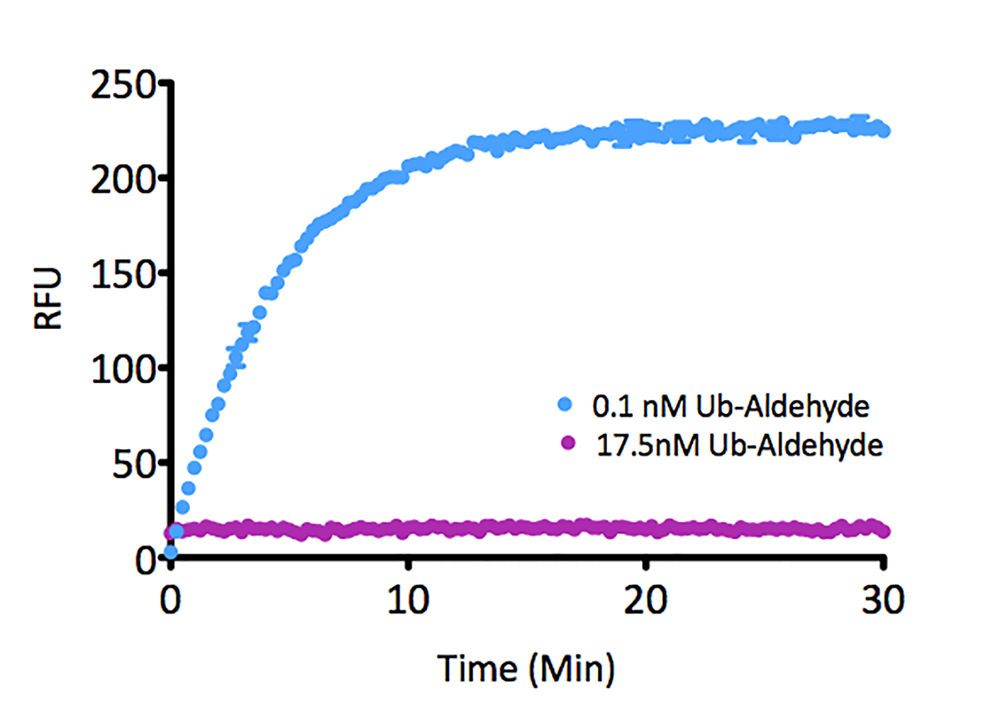
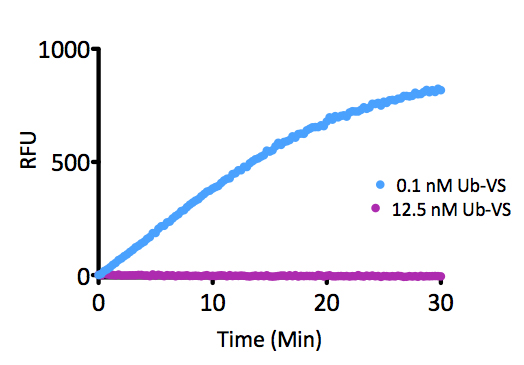
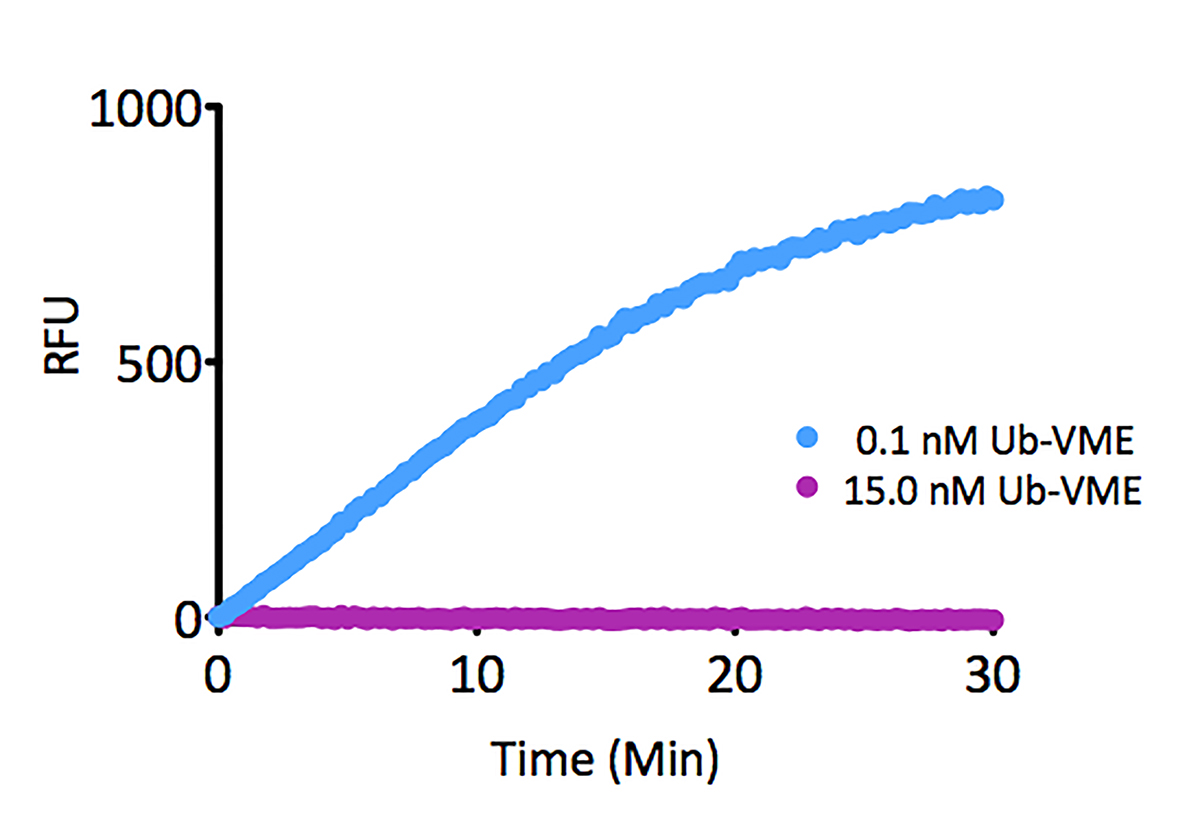
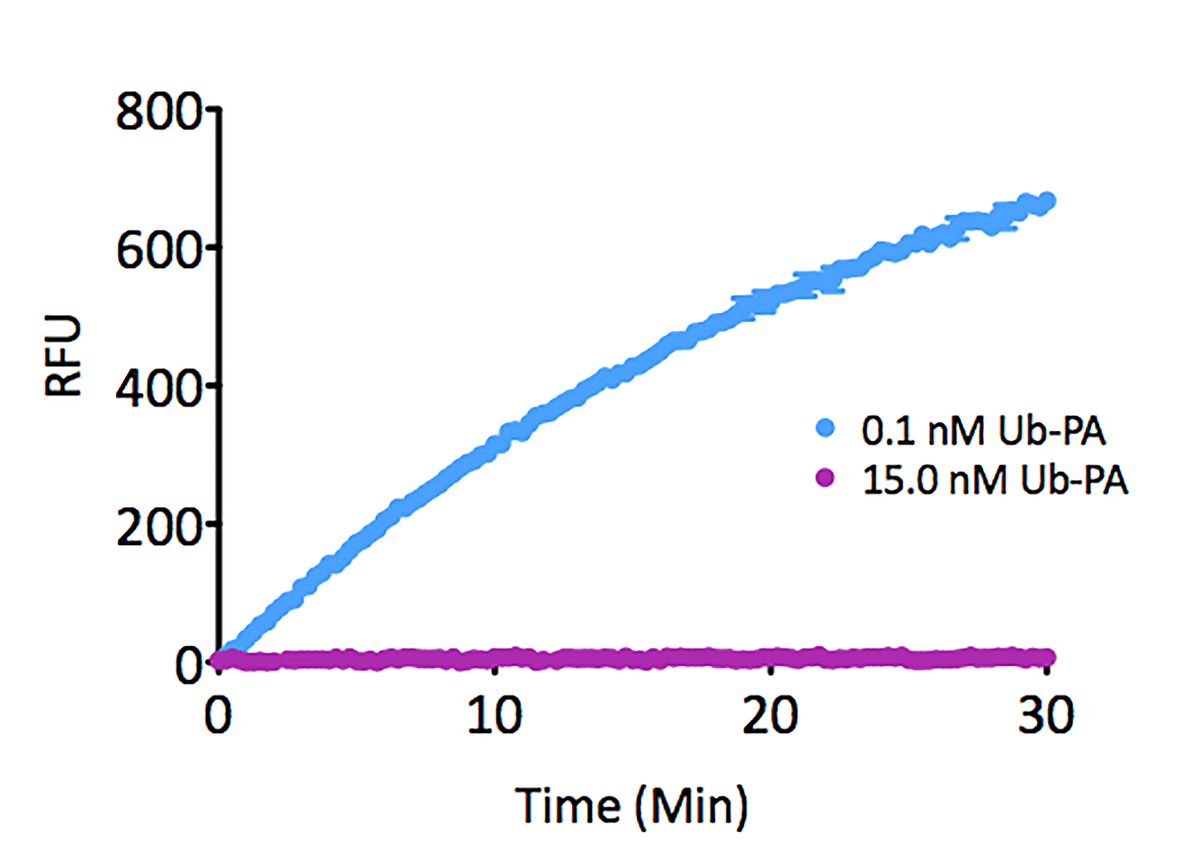
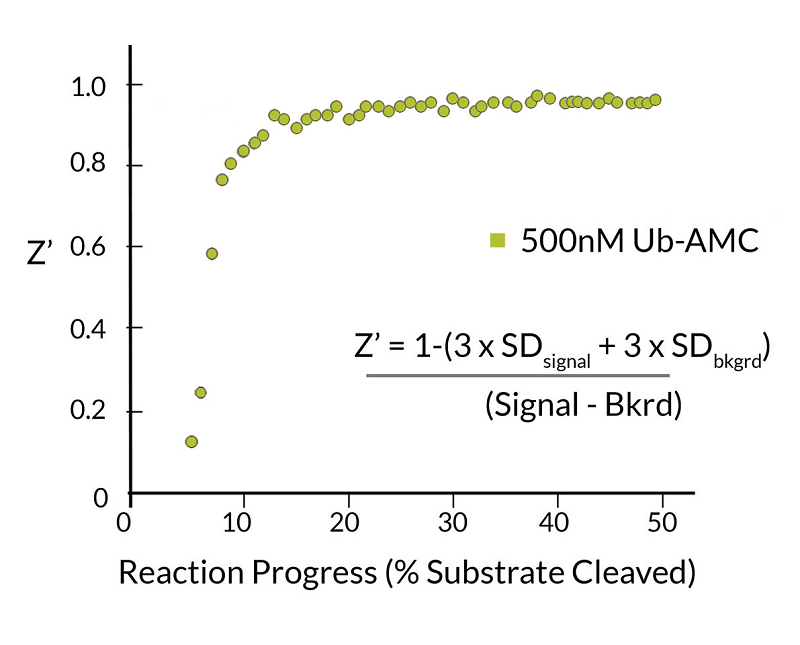
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Protein. Full-length, mature ubiquitin polypeptide (amino acids 1-76) conjugated on its C-terminus to AMC. Source/Host: E. coli. Liquid. In 50mM MES pH 6.0. Ubiquitin is a 76 amino acid post-translational modifier expressed throughout all tissues in eukaryotic organisms. The many roles of ubiquitin modification include proteasomal degradation, signal transduction, inflammatory response, and DNA damage repair. Ubiquitin modification occurs through a pyramidal cascade of an E1 activating enzyme, E2 conjugating enzymes, and an E3 ubiquitin ligases. This enzymatic cascade results in modification of a epsilon-amine of a lysine residue on a substrate protein. Substrates may either be mono or poly-ubiquitinated by M1, K6, 11, 27, 29, 33, 48 or 63 linkages. Removal of ubiquitin from a substrate protein occurs via deconjugating enzymes, of which there are nearly 100 known enzymes with various specificities. - Ubiquitin is a 76 amino acid post-translational modifier expressed throughout all tissues in eukaryotic organisms. The many roles of ubiquitin modification include proteasomal degradation, signal transduction, inflammatory response, and DNA damage repair. Ubiquitin modification occurs through a pyramidal cascade of an E1 activating enzyme, E2 conjugating enzymes, and an E3 ubiquitin ligases. This enzymatic cascade results in modification of a epsilon-amine of a lysine residue on a substrate protein. Substrates may either be mono or poly-ubiquitinated by M1, K6, 11, 27, 29, 33, 48 or 63 linkages. Removal of ubiquitin from a substrate protein occurs via deconjugating enzymes, of which there are nearly 100 known enzymes with various specificities.
- Storage Instruction-80°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman

![Ubiquitin Activating Enzyme E1 [UBA1; UBE1] (human) (rec.) (His)](https://adipogen.com/pub/media/catalog/product/s/b/sbb-ce0058_finalgel.png)