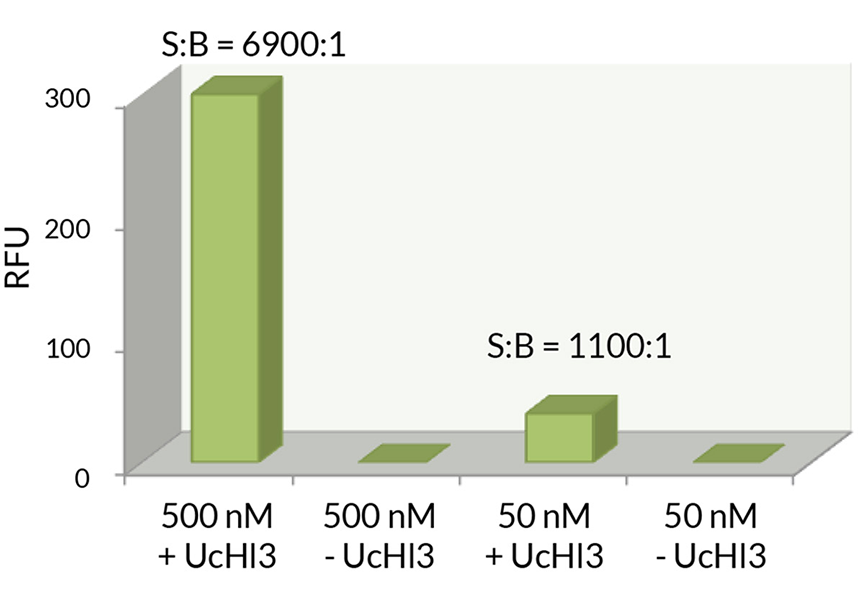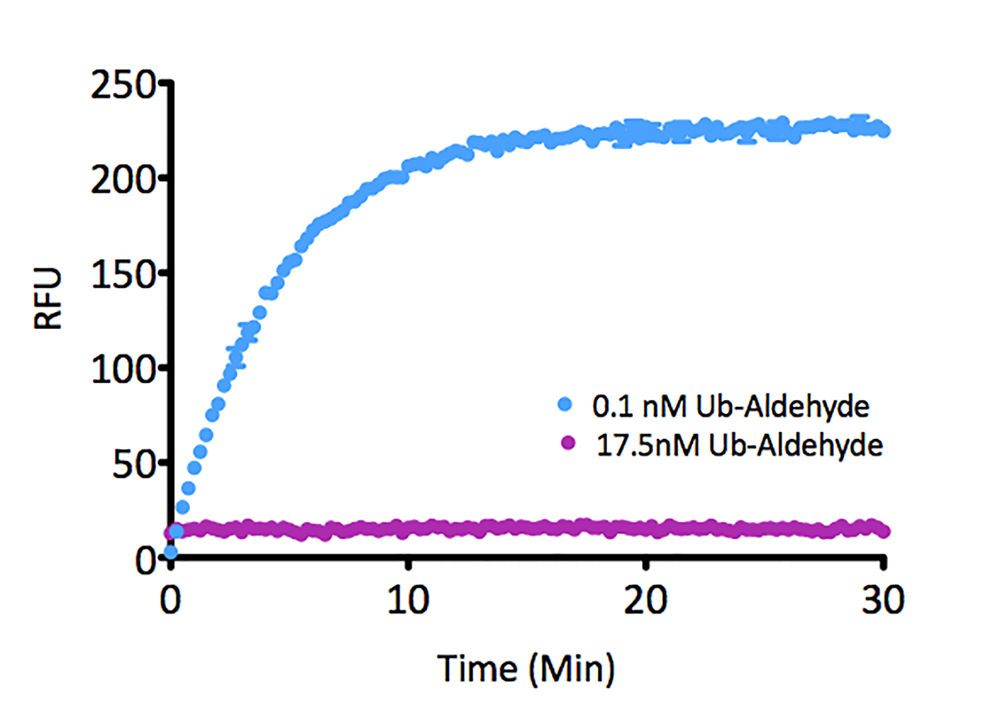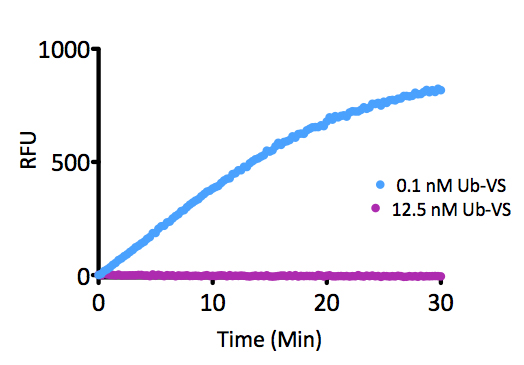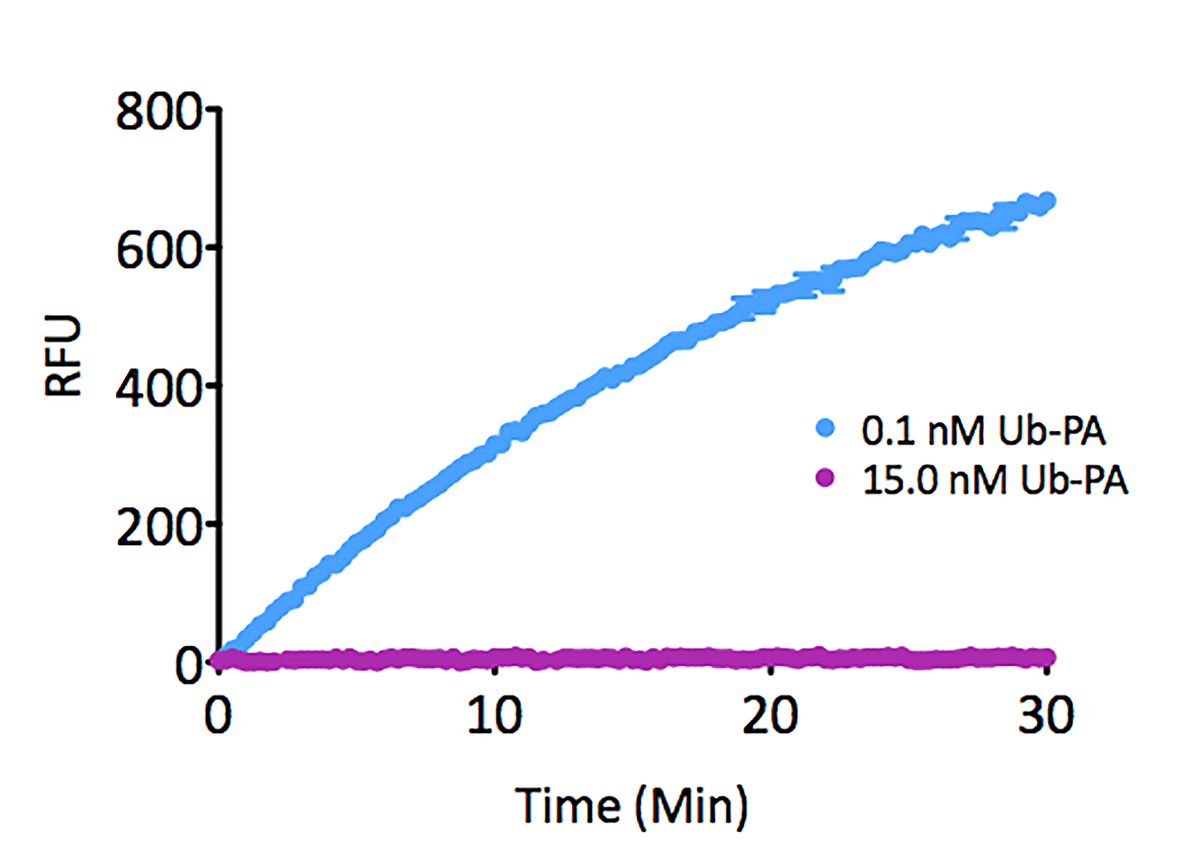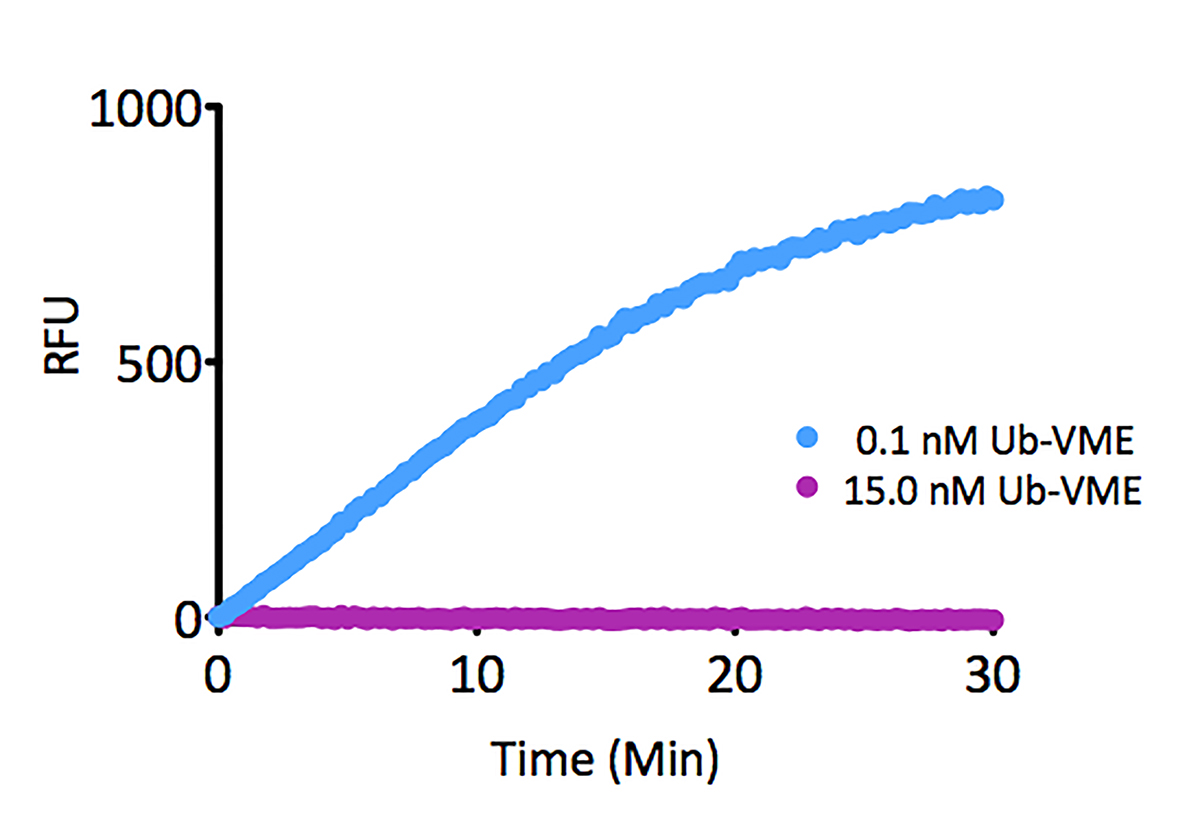
Kinetic Activity: UCHL3 (SBB-DE0023) activity with Ubiquitin-AMC (SBB-PS0043) measured in the presence of 15.0nM and 0.1nM Ubiquitin vinyl methyl ester (SBB-PS0033).
Ubiquitin vinyl methyl ester (human) (rec.)
SBB-PS0033
Protein IDP0CG47
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierSouth Bay Bio
- Product NameUbiquitin vinyl methyl ester (human) (rec.)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Gene ID7314
- Target nameUBB
- Target descriptionubiquitin B
- Target synonymsHEL-S-50, polyubiquitin-B, epididymis secretory protein Li 50, polyubiquitin B
- Protein IDP0CG47
- Protein NamePolyubiquitin-B
- Scientific DescriptionProtein. Human ubiquitin (aa1-76)with a C-terminal vinyl methyl ester group. Source: E. coli. Formulation: Liquid. In 50mM MES pH 6.0, 100mM sodium chloride. Purity: >97% (LCMS). Ubiquitin is a small (8.5kDa) regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotic organisms. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination or ubiquitylation. Ubiquitination can affect proteins in many ways: it can signal for their degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity and promote or prevent protein interactions. Removal of ubiquitin from a substrate protein occurs via deconjugating enzymes, of which there are nearly 100 known enzymes with various linkage specificities. This product consists of a full-length human, mature ubiquitin polypeptide (amino acids 1-76), expressed in E.coli with a C-terminal warhead (Vinyl Methyl Ester). Ubiquitin vinyl methyl ester is a potent, irreversible and specific inhibitor of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) based on a C-terminal electrophilic vinyl methyl ester group. Ubiquitin vinyl methyl ester can be used for activity profiling experiments and determining DUB inhibitor specificity. It targets three of the four major DUB families: UCH (Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases), USP (Ubiquitin specific proteases), OTU (Ovarian tumor proteases) and MJD (Machado-Josephin domain proteases) while JAMM metalloproteases are not inhibited. - Ubiquitin is a small (8.5kDa) regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotic organisms. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination or ubiquitylation. Ubiquitination can affect proteins in many ways: it can signal for their degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity and promote or prevent protein interactions. Removal of ubiquitin from a substrate protein occurs via deconjugating enzymes, of which there are nearly 100 known enzymes with various linkage specificities. This product consists of a full-length human, mature ubiquitin polypeptide (amino acids 1-76), expressed in E.coli with a C-terminal warhead (Vinyl Methyl Ester). Ubiquitin vinyl methyl ester is a potent, irreversible and specific inhibitor of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) based on a C-terminal electrophilic vinyl methyl ester group. Ubiquitin vinyl methyl ester can be used for activity profiling experiments and determining DUB inhibitor specificity. It targets four of the five major DUB families: UCH (Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases), USP (Ubiquitin specific proteases), OTU (Ovarian tumor proteases) and MJD (Machado-Josephin domain proteases) while JAMM metalloproteases are not inhibited.
- Storage Instruction-80°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman

![Ubiquitin Activating Enzyme E1 [UBA1; UBE1] (human) (rec.) (His)](https://adipogen.com/pub/media/catalog/product/s/b/sbb-ce0058_finalgel.png)