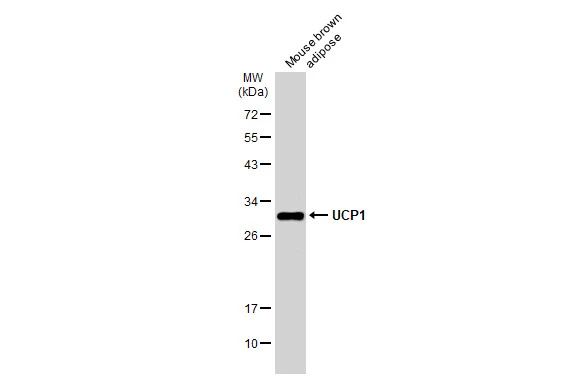
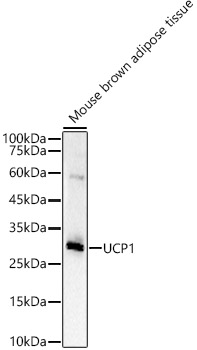
Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with UCP1 antibody (GTX112784) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
UCP1 antibody
GTX112784
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetUCP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameUCP1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.34 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7350
- Target nameUCP1
- Target descriptionuncoupling protein 1
- Target synonymsSLC25A7, UCP, mitochondrial brown fat uncoupling protein 1, solute carrier family 25 member 7, thermogenin, uncoupling protein 1 (mitochondrial, proton carrier)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP25874
- Protein NameMitochondrial brown fat uncoupling protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionMitochondrial uncoupling proteins (UCP) are members of the family of mitochondrial anion carrier proteins (MACP). UCPs separate oxidative phosphorylation from ATP synthesis with energy dissipated as heat, also referred to as the mitochondrial proton leak. UCPs facilitate the transfer of anions from the inner to the outer mitochondrial membrane and the return transfer of protons from the outer to the inner mitochondrial membrane. They also reduce the mitochondrial membrane potential in mammalian cells. Tissue specificity occurs for the different UCPs and the exact methods of how UCPs transfer H+/OH- are not known. UCPs contain the three homologous protein domains of MACPs. This gene is expressed only in brown adipose tissue, a specialized tissue which functions to produce heat. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161




![Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with UCP1 antibody [HL2944] (GTX640329) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX640329/GTX640329_45460_20240705_WB_M_tissue_24070822_603.webp)