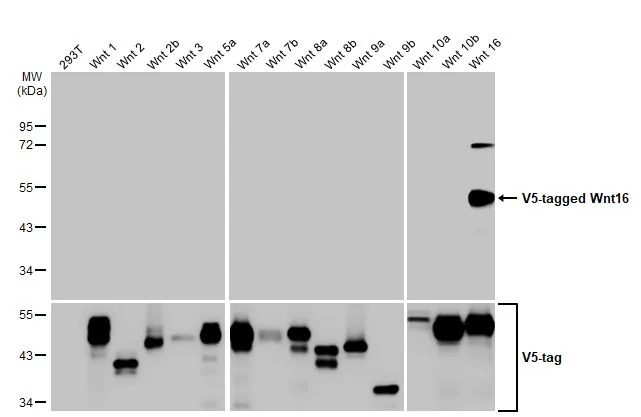
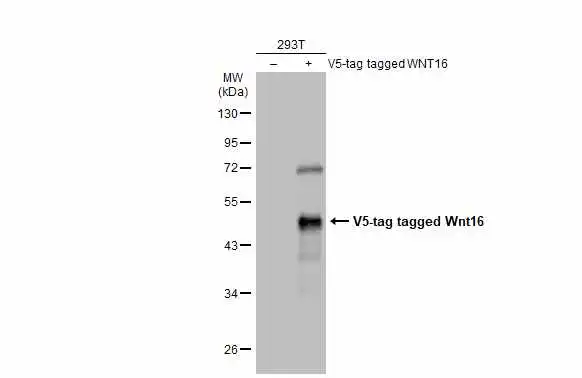
Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Wnt16 antibody (GTX128468) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
Wnt16 antibody
GTX128468
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetWNT16
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameWnt16 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.65 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID51384
- Target nameWNT16
- Target descriptionWnt family member 16
- Target synonymsprotein Wnt-16, wingless-type MMTV integration site family member 16b, wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 16
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UBV4
- Protein NameProtein Wnt-16
- Scientific DescriptionThe WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It contains two transcript variants diverging at the 5 termini. These two variants are proposed to be the products of separate promoters and not to be splice variants from a single promoter. They are differentially expressed in normal tissues, one of which (variant 2) is expressed at significant levels only in the pancreas, whereas another one (variant 1) is expressed more ubiquitously with highest levels in adult kidney, placenta, brain, heart, and spleen. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161






![Wnt16 antibody [HL1498] detects Wnt16 protein by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: Mock and transfected 293T cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Wnt16 stained by Wnt16 antibody [HL1498] (GTX636972) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX636972/GTX636972_44746_20220916_ICC_IF_B_22102723_435.webp)