
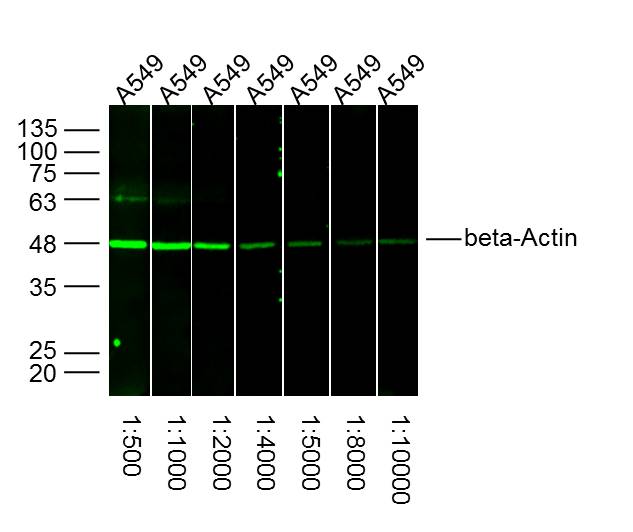
1:1000 (1microg/mL) Ab dilution used in WB of 20microg/lane tissue lysates from human (1), mouse (2), rat (3), and rabbit (4)
Actin antibody [BA3R]
GTX82559
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityChicken, Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat
TargetACTB
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameActin antibody [BA3R]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteRecommended Starting Dilutions:WB (with ECL): Use at a dilution of 1:1000-10000 Immunostaining: Use at a dilution of 1:500 - 1:2000For best results with other assays (e.g.: Dot, ELISA, IP, etc), please determine optimal working dilution by titration test
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDBA3R
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID60
- Target nameACTB
- Target descriptionactin beta
- Target synonymsBKRNS, BNS, BRWS1, CSMH, DDS1, PS1TP5BP1, THC8, actin, cytoplasmic 1, I(2)-actin, PS1TP5-binding protein 1, beta cytoskeletal actin
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Scientific DescriptionActin is a ubiquitous globular protein that is one of the most highly-conserved proteins known. It is foundin two main states; G-actin is the globular monomeric form, whereas F-actin forms helical polymers. Both G-and F-actin are intrinsically flexible structures - a feature vital in actins role as a dynamic filamentnetwork. Actin has four major functions. Firstly, F-actin polymers form microfilaments - polar intracellulartracks for kinesin motor proteins, allowing the transport of vesicles, organelles and other cargo. Actinis a component of the cytoskeleton and links to alpha-actinin, E-cadherin and beta-catenin at adherensjunctions. This gives mechanical support to cells and attaches them to each other and the extracellularmatrix. In muscle cells, actin-rich thin filaments associate with myosin-rich thick filaments to formactomyosin myofibrils. Using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP, myofibrils undergo cyclic shortening throughactin-myosin head interactions, which represents the mechanics of muscle contraction. Finally, actin has arole in cell motility through polymerization and depolymerization of fibrils.
- ReactivityChicken, Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Valle-Bautista R, Márquez-Valadez B, Herrera-López G, et al. Long-Term Functional and Cytoarchitectonic Effects of the Systemic Administration of the Histamine H(1) Receptor Antagonist/Inverse Agonist Chlorpheniramine During Gestation in the Rat Offspring Primary Motor Cortex. Front Neurosci. 2021,15:740282. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.740282Read this paper





![FACS analysis of MCF-7 cells using GTX83163 beta Actin antibody [8H10D10]. Right : beta Actin Left : negative control](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83163/GTX83163_20170912_FACS_w_23061322_375.webp)