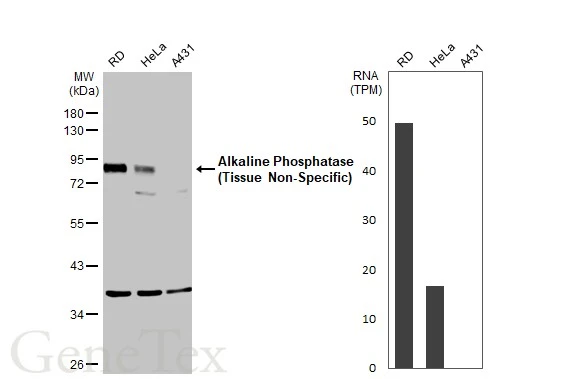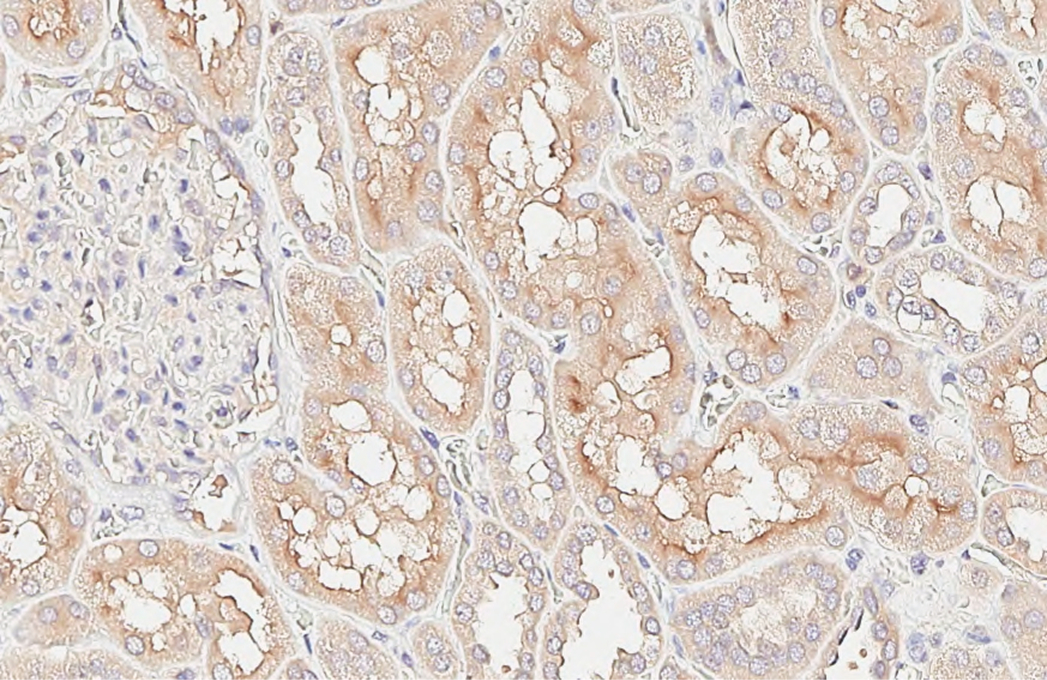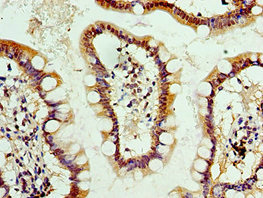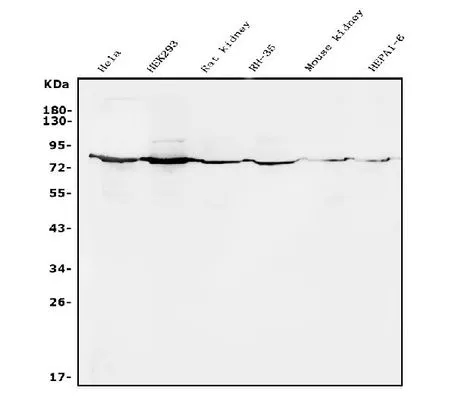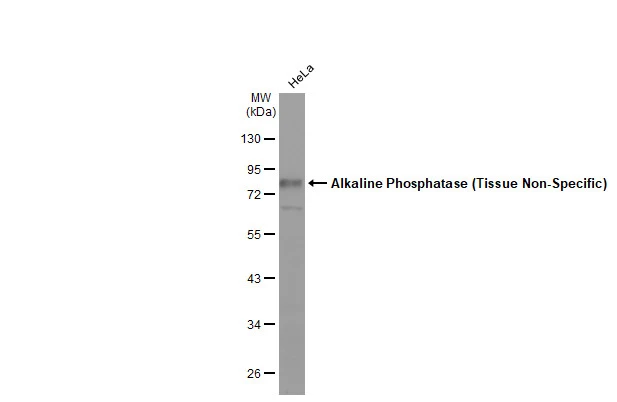
Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Alkaline Phosphatase (Tissue Non-Specific) antibody (GTX100817) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
Alkaline Phosphatase (Tissue Non-Specific) antibody
GTX100817
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Sheep
TargetALPL
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameAlkaline Phosphatase (Tissue Non-Specific) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID249
- Target nameALPL
- Target descriptionalkaline phosphatase, biomineralization associated
- Target synonymsAP-TNAP, APTNAP, HOPS, HPPA, HPPC, HPPI, HPPO, TNALP, TNAP, TNS-ALP, TNSALP, alkaline phosphatase, tissue-nonspecific isozyme, alkaline phosphatase liver/bone/kidney isozyme, alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney, liver/bone/kidney-type alkaline phosphatase, phosphoamidase, phosphocreatine phosphatase, tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase, tissue-nonspecific ALP
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP05186
- Protein NameAlkaline phosphatase, tissue-nonspecific isozyme
- Scientific DescriptionThere are at least four distinct but related alkaline phosphatases: intestinal, placental, placental-like, and liver/bone/kidney (tissue non-specific). The first three are located together on chromosome 2, while the tissue non-specific form is located on chromosome 1. The product of this gene is a membrane bound glycosylated enzyme that is not expressed in any particular tissue and is, therefore, referred to as the tissue-nonspecific form of the enzyme. The exact physiological function of the alkaline phosphatases is not known. A proposed function of this form of the enzyme is matrix mineralization; however, mice that lack a functional form of this enzyme show normal skeletal development. This enzyme has been linked directly to hypophosphatasia, a disorder that is characterized by hypercalcemia and includes skeletal defects. The character of this disorder can vary, however, depending on the specific mutation since this determines age of onset and severity of symptoms. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, which encode the same protein, have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Sheep
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161