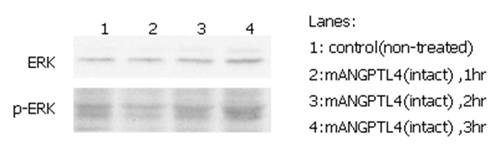
ERK phosphorylation induced by hANGPTL4 in THP-1 cells. THP-1 monocyte cells were serum starved for 16hr and then stimulated with ANGPTL4 (mouse) (rec.) (Prod. No. AG-40A-0075) (500ng/ml) for 1, 2 and 3 hrs, respectively. Antibodies against pERK1/2
ANGPTL4 (mouse) (rec.)
AG-40A-0075
Protein IDQ9Z1P8
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameANGPTL4 (mouse) (rec.)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Gene ID57875
- Target nameAngptl4
- Target descriptionangiopoietin-like 4
- Target synonymsArp4, Bk89, Fiaf, Hfarp, Ng27, Pgar, Pgarg, Pp1158, angiopoietin-related protein 4, 425O18-1, angiopoietin-like protein 4, fasting-induced adipose factor, fibrinogen/angiopoietin-related protein, hepatic fibrinogen/angiopoietin-related protein, major histocompatibility complex region NG27, secreted protein Bk89
- Protein IDQ9Z1P8
- Protein NameAngiopoietin-related protein 4
- Scientific DescriptionANGPTL4 (Angiopoietin-like protein 4) mainly expressed in endothelial cells (hypoxia-induced). Regulates angiogenesis and modulates tumorigenesis and directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. Inhibits proliferation, migration, and tubule formation of endothelial cells and reduces vascular leakage. ANGPTL4 is a protein consisting of an N-terminal coiled-coil domain and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain (FLD). Both domains have distinct biological functions. The coiled-coil domain is responsible for the inhibitory effects on lipoprotein lipase (LPL) converting the active form of LPL into an inactive form, and the FLD domain mediates its antiangiogenic functions. The coiled coil and the FLD domains are separated by a short linker that can be cleaved after secretion. ANGPTL4 appears on the cell surface as the full-length form, where it can be released by heparin treatment. ANGPTL4 protein is then proteolytically cleaved by proprotein convertases (PCs), including furin, PC5/6, paired basic amino acid-cleaving enzyme 4, and PC7. - Protein. Mouse ANGPTL4 (aa 1-410) is fused at the C-terminus to a FLAG®-tag. Source: COS-7 cells. Endotoxin content: 90% (SDS-PAGE). ANGPTL4 (Angiopoietin-like protein 4) mainly expressed in endothelial cells (hypoxia-induced). Regulates angiogenesis and modulates tumorigenesis and directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. Inhibits proliferation, migration, and tubule formation of endothelial cells and reduces vascular leakage. ANGPTL4 is a protein consisting of an N-terminal coiled-coil domain and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain (FLD). Both domains have distinct biological functions. The coiled-coil domain is responsible for the inhibitory effects on lipoprotein lipase (LPL) converting the active form of LPL into an inactive form, and the FLD domain mediates its antiangiogenic functions. The coiled coil and the FLD domains are separated by a short linker that can be cleaved after secretion. ANGPTL4 appears on the cell surface as the full-length form, where it can be released by heparin treatment. ANGPTL4 protein is then proteolytically cleaved by proprotein convertases (PCs), including furin, PC5/6, paired basic amino acid-cleaving enzyme 4, and PC7.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesMouse

