Anti-ACADM Antibody
ER1804-01
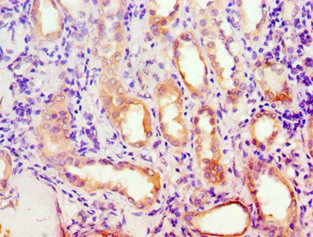
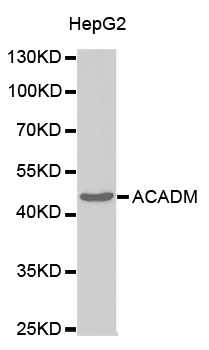
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetACADM
Overview
- SupplierHUABIO
- Product NameAnti-ACADM Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer7
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- Applications SupplierWB,IF-Cell,IHC-P,FC
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID34
- Target nameACADM
- Target descriptionacyl-CoA dehydrogenase medium chain
- Target synonymsACAD1, MCAD, MCADH, medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, C-4 to C-12 straight chain, acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, C-4 to C-12 straight chain, medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, testicular tissue protein Li 7
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP11310
- Protein NameMedium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionACADM (acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, C-4 to C-12 straight chain) is a gene that provides instructions for making an enzyme called acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase that is important for breaking down (degrading) a certain group of fats called medium-chain fatty acids. These fatty acids are found in foods such as milk and certain oils, and they are also stored in the bodys fat tissue. Medium-chain fatty acids are also produced when larger fatty acids are degraded. The acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase for medium-chain fatty acids (ACADM) enzyme is essential for converting these particular fatty acids to energy, especially during periods without food (fasting). The ACADM enzyme functions in mitochondria, the energy-producing centers within cells. It is found in the mitochondria of several types of tissues, particularly the liver. The LCAD enzyme catalyzes most of fatty acid beta-oxidation by forming a C2-C3 trans-double bond in the fatty acid. MCAD works on long-chain fatty acids, typically between C4 and C12-acylCoA. Fatty acid oxidation has proven to spare glucose in fasting conditions, and is also required for amino acid metabolism, which is essential for the maintenance of adequate glucose production.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Reactivity SupplierHuman,Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161