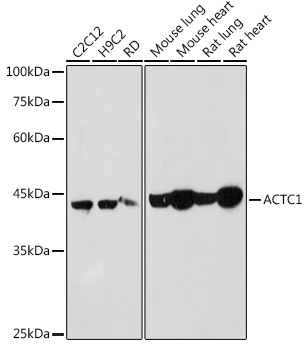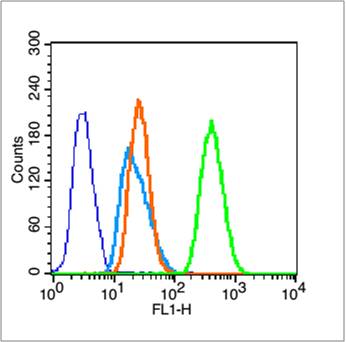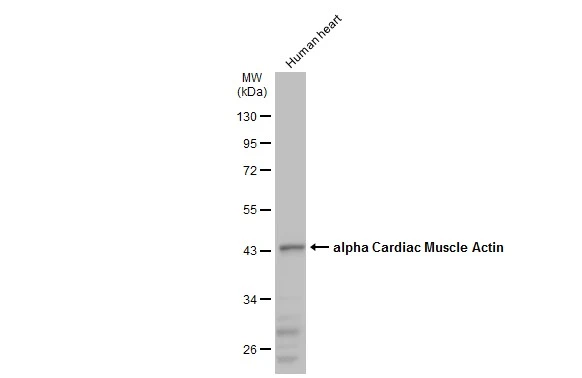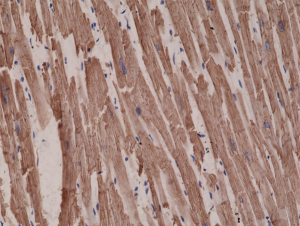
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human heart tissue sections using Anti-alpha-cardiac actin rabbit monoclonal antibody, Clone RM257 at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-Alpha Cardiac Actin, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM257)
REV-31-1138-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetACTC1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Alpha Cardiac Actin, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM257)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM257
- Gene ID70
- Target nameACTC1
- Target descriptionactin alpha cardiac muscle 1
- Target synonymsACTC, ASD5, CMD1R, CMH11, LVNC4, actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP68032
- Protein NameActin, alpha cardiac muscle 1
- Scientific DescriptionActins are a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments and are important for cell movement and the tensing (contraction) of muscles. ACTC1 (Cardiac alpha actin) together with regulatory proteins tropomyosin and 3 troponins (C, I, and T) forms the thin contractile filament, in turn connecting the myocellular Z-disc with the thick filament protein myosin. Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to four others. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the actin family which is comprised of three main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta and gamma. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. Defects in this gene have been associated with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDC) and familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC). Mutations in ACTC1 are associated in autosomal dominant heart failure and familial atrial septal defect (ASD). Cardiac (ACTC1) and skeletal (ACTA1) alpha actins differ by only four amino acids (Asp4Glu, Glu5Asp, Leu301Met, Ser360Thr; cardiac/skeletal). - Recombinant Antibody. The antibody reacts to human and mouse alpha cardiac actin (Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1). This antibody may also react to bovine or rat alpha-cardiac actin, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Actins are a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments and are important for cell movement and the tensing (contraction) of muscles. ACTC1 (Cardiac alpha actin) together with regulatory proteins tropomyosin and 3 troponins (C, I, and T) forms the thin contractile filament, in turn connecting the myocellular Z-disc with the thick filament protein myosin. Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to four others. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the actin family which is comprised of three main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta and gamma. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. Defects in this gene have been associated with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDC) and familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC). Mutations in ACTC1 are associated in autosomal dominant heart failure and familial atrial septal defect (ASD). Cardiac (ACTC1) and skeletal (ACTA1) alpha actins differ by only four amino acids (Asp4Glu, Glu5Asp, Leu301Met, Ser360Thr; cardiac/skeletal).
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161