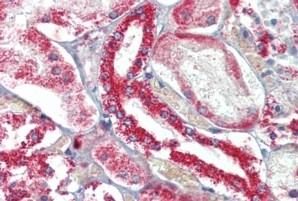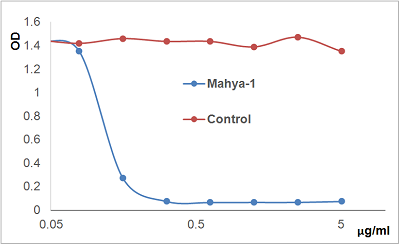
anti-APRIL (human), mAb (blocking) (Mahya-1) (preservative free)
AG-20B-0078PF
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, ELISA, Neutralisation/Blocking
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTNFSF13
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-APRIL (human), mAb (blocking) (Mahya-1) (preservative free)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, ELISA, Neutralisation/Blocking
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDMahya-1
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID8741
- Target nameTNFSF13
- Target descriptionTNF superfamily member 13
- Target synonymsAPRIL, CD256, TALL-2, TALL2, TNLG7B, TRDL-1, UNQ383/PRO715, ZTNF2, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13, TNF- and APOL-related leukocyte expressed ligand 2, a proliferation-inducing ligand, tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13, tumor necrosis factor ligand 7B, tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 13, tumor necrosis factor-like protein ZTNF2, tumor necrosis factor-related death ligand-1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDO75888
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13
- Scientific DescriptionMonoclonal Antibody. Recognizes human APRIL. Does not recognize mouse APRIL or mouse and human BAFF. Applications: ELISA, FUNC (Blocking), IP. Isotype: Mouse IgG1 kappa. Clone: Mahya-1. Liquid. In PBS. The B cell-stimulating molecules, BAFF (B cell activating factor) and APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand), are critical factors in the maintenance of the B cell pool and humoral immunity. APRIL binds to transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), B cell maturation antigen (BCMA), and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) within the extracellular matrix or on the surface of cells such as plasma cells. APRIL maintains B cell homeostasis by acting at a later stage, modulating the function and survival of antigen-experienced B cells. APRIL (as well as BAFF) stimulates class-switch recombination (CSR), hence contributes to shaping humoral effector mechanisms. With regards to humoral memory, APRIL is involved in the establishment and survival of the long-lived plasma cell (LLPC) pool in the bone marrow (BM). APRIL is expressed by a number of myeloid-derived cell types including BM granulocytes, megakaryocytes, eosinophils and osteoclasts and by dendritic cells following exposure to IFNalpha, IFNgamma or CD40L. APRIL expression is induced during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. APRIL expression is not limited to cells of myeloid origin, but can also be found in epithelial cells of the gut, tonsil, breast and skin. Finally, APRIL is expressed in tumor cell lines and human cancer cells of colon, thyroid and lymphoid origin. APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand) is implicated in several human autoimmune diseases with autoreactive B cell involvement, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjoegrens syndrome (SS), IgA nephropathy (IgAN) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). APRIL might also function in enhancing proliferation of some tumor cells, especially B-cell malignancies. - The B cell-stimulating molecules, BAFF (B cell activating factor) and APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand), are critical factors in the maintenance of the B cell pool and humoral immunity. APRIL binds to transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), B cell maturation antigen (BCMA), and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) within the extracellular matrix or on the surface of cells such as plasma cells. APRIL maintains B cell homeostasis by acting at a later stage, modulating the function and survival of antigen-experienced B cells. APRIL (as well as BAFF) stimulates class-switch recombination (CSR), hence contributes to shaping humoral effector mechanisms. With regards to humoral memory, APRIL is involved in the establishment and survival of the long-lived plasma cell (LLPC) pool in the bone marrow (BM). APRIL is expressed by a number of myeloid-derived cell types including BM granulocytes, megakaryocytes, eosinophils and osteoclasts and by dendritic cells following exposure to IFN-alpha, IFN-gamma or CD40L. APRIL expression is induced during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. APRIL expression is not limited to cells of myeloid origin, but can also be found in epithelial cells of the gut, tonsil, breast and skin. Finally, APRIL is expressed in tumor cell lines and human cancer cells of colon, thyroid and lymphoid origin. APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand) is implicated in several human autoimmune diseases with autoreactive B cell involvement, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjoegrens syndrome (SS), IgA nephropathy (IgAN) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). APRIL might also function in enhancing proliferation of some tumor cells, especially B cell malignancies.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161