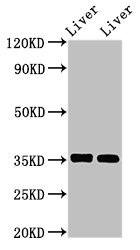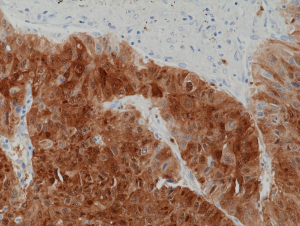
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human liver cancer tissue section using anti-ARG1 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM377) at a 1:1250 dilution.
anti-Arginase-1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM377)
REV-31-1263-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetARG1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Arginase-1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM377)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM377
- Gene ID383
- Target nameARG1
- Target descriptionarginase 1
- Target synonymsarginase-1, arginase, liver, liver-type arginase, type I arginase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP05089
- Protein NameArginase-1
- Scientific DescriptionArginase I, encoded by the ARG1 gene, is a cytosolic metalloenzyme expressed predominantly in hepatocytes which plays a key role in the urea cycle by catalyzing the hydrolysis of arginine to ornithine and urea. Inherited deficiency of this enzyme results in argininemia, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hyperammonemia, a buildup of arginine and ammonia in the blood. Arginase is involved in the nitric oxide (NO) pathway and immune cell arginine metabolism. It is fundamentally involved in cancer, inflammation, infections, fibrotic diseases, neurobiology, pregnancy and immune regulation in general. Anti-Arginase I is highly specific for hepatocytes and is therefore a sensitive and specific marker of benign and malignant hepatic tumors. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Arginase-1 (ARG1). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Arginase I, encoded by the ARG1 gene, is a cytosolic metalloenzyme expressed predominantly in hepatocytes which plays a key role in the urea cycle by catalyzing the hydrolysis of arginine to ornithine and urea. Inherited deficiency of this enzyme results in argininemia, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hyperammonemia, a buildup of arginine and ammonia in the blood. Arginase is involved in the nitric oxide (NO) pathway and immune cell arginine metabolism. It is fundamentally involved in cancer, inflammation, infections, fibrotic diseases, neurobiology, pregnancy and immune regulation in general. Anti-Arginase I is highly specific for hepatocytes and is therefore a sensitive and specific marker of benign and malignant hepatic tumors.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161