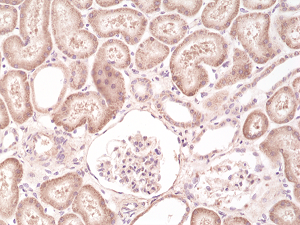
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human kidney tissue section using anti-B-raf rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM308) at a 1:500 dilution.
anti-BRAF (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM308)
REV-31-1194-00
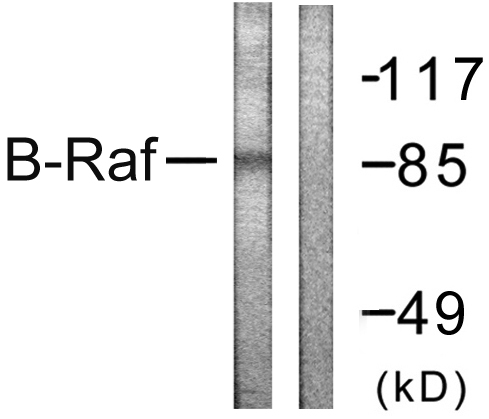
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetBRAF
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-BRAF (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM308)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM308
- Gene ID673
- Target nameBRAF
- Target descriptionB-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase
- Target synonymsB-RAF1, B-raf, BRAF-1, BRAF1, NS7, RAFB1, serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf, 94 kDa B-raf protein, B-Raf proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase (p94), B-Raf serine/threonine-protein, murine sarcoma viral (v-raf) oncogene homolog B1, proto-oncogene B-Raf, v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP15056
- Protein NameSerine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf
- Scientific DescriptionBRAF is a human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf. B-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of growth signal transduction protein kinases. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase/ERKs signaling pathway, which affects cell division, differentiation and secretion. Mutations in the BRAF gene can cause birth defects (inherited) or cancer, as an oncogene. Mutations in this gene have been found in cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma, colorectal cancer, malignant melanoma, papillary thyroid carcinoma, non-small-cell lung carcinoma, adenocarcinoma of the lung, brain tumors including glioblastoma and Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytomas as well as inflammatory diseases like erdheim-chester disease. The majority (>90%) of BRAF mutant cancers harbor the V600E mutation. The mutation leads to activation of the MAPK signaling pathway that increases cell invasion and reduces apoptosis. It also leads to reduced expression of melanocyte differentiation antigens and subsequent immune evasion - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF). It may also react to mouse B-raf, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. BRAF is a human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf. B-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of growth signal transduction protein kinases. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase/ERKs signaling pathway, which affects cell division, differentiation and secretion. Mutations in the BRAF gene can cause birth defects (inherited) or cancer, as an oncogene. Mutations in this gene have been found in cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma, colorectal cancer, malignant melanoma, papillary thyroid carcinoma, non-small-cell lung carcinoma, adenocarcinoma of the lung, brain tumors including glioblastoma and Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytomas as well as inflammatory diseases like erdheim-chester disease. The majority (>90%) of BRAF mutant cancers harbor the V600E mutation. The mutation leads to activation of the MAPK signaling pathway that increases cell invasion and reduces apoptosis. It also leads to reduced expression of melanocyte differentiation antigens and subsequent immune evasion
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161





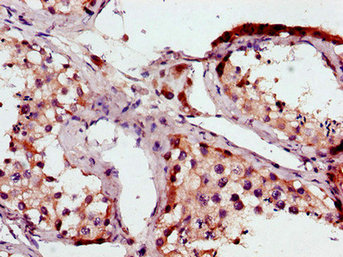
![B-Raf antibody [N2C1], Internal detects B-Raf protein at cytosol on mouse testis by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse testis. B-Raf antibody [N2C1], Internal (GTX100913) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100913/GTX100913_39471_IHC_M_w_23060100_112.webp)