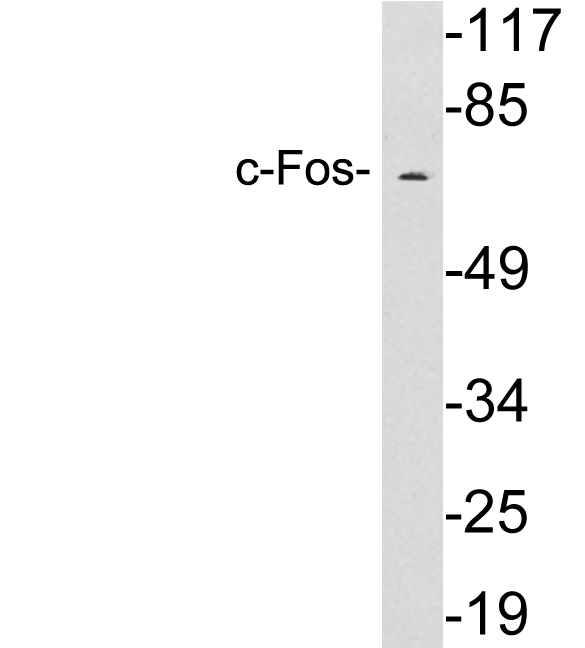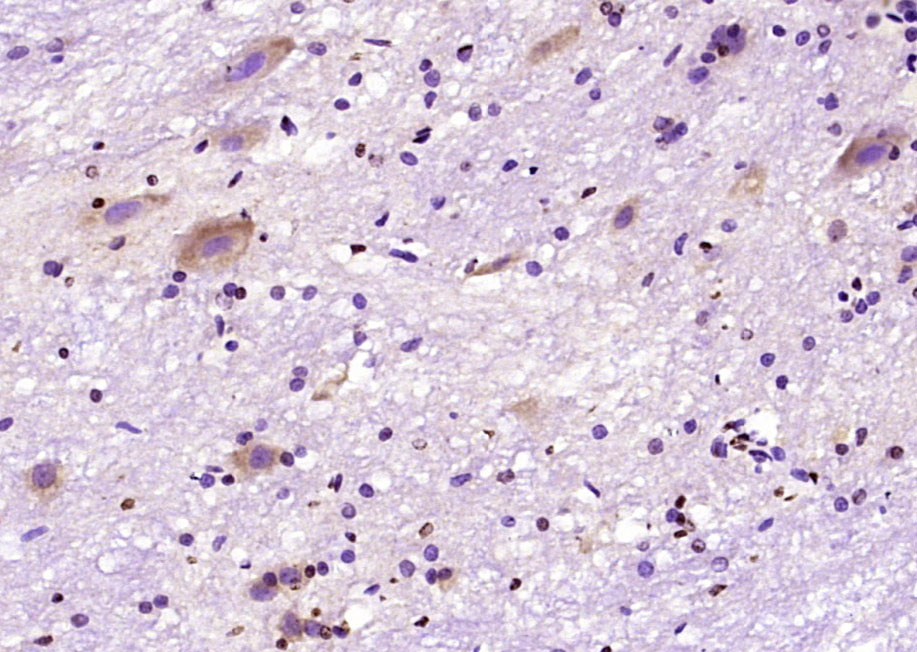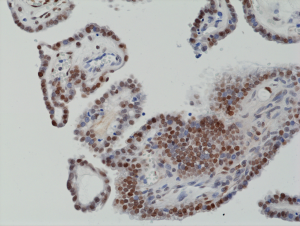
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human thyroid tissue section using anti-c-Fos rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM374) at a 1:1250 dilution.
anti-c-Fos (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM374)
REV-31-1260-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetFOS
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-c-Fos (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM374)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM374
- Gene ID2353
- Target nameFOS
- Target descriptionFos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit
- Target synonymsAP-1, C-FOS, p55, protein c-Fos, FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral (v-fos) oncogene homolog (oncogene FOS), FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog, Fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 trancription factor subunit, G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 7, activator protein 1, cellular oncogene c-fos, proto-oncogene c-Fos, transcription factor AP-1 subunit c-Fos
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01100
- Protein NameProtein c-Fos
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Proto-oncogene c-Fos. It may also react to mouse and rat c-Fos, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The Fos family of nuclear oncogenes includes c-Fos, FosB, Fos-related antigen 1 (FRA1) and Fos-related antigen 2 (FRA2). The expression of Fos proteins is rapidly and transiently induced by a variety of extracellular stimuli including growth factors, cytokines, neurotransmitters, polypeptide hormones and stress. Fos proteins dimerize with Jun proteins (c-Jun, JunB, and JunD) to form Activator Protein-1 (AP-1), a transcription factor that binds to TRE/AP-1 elements and activates transcription of several genes that play an important role in cellular signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. c-Fos has been shown to be phosphorylated by various stimuli including growth factors and insulin at atleast seven different sites. The best known upstream kinase for phosphorylation at Thr232 is ERK MAPK which regulates localization of c-Fos to the nucleus and is thus important for c-Fos induced transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation of c-Fos at Ser32 and Thr232 by Erk5 increases protein stability and nuclear localization. c-Fos plays an important role in many cellular functions and has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers. - The Fos family of nuclear oncogenes includes c-Fos, FosB, Fos-related antigen 1 (FRA1) and Fos-related antigen 2 (FRA2). The expression of Fos proteins is rapidly and transiently induced by a variety of extracellular stimuli including growth factors, cytokines, neurotransmitters, polypeptide hormones and stress. Fos proteins dimerize with Jun proteins (c-Jun, JunB, and JunD) to form Activator Protein-1 (AP-1), a transcription factor that binds to TRE/AP-1 elements and activates transcription of several genes that play an important role in cellular signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. c-Fos has been shown to be phosphorylated by various stimuli including growth factors and insulin at atleast seven different sites. The best known upstream kinase for phosphorylation at Thr232 is ERK MAPK which regulates localization of c-Fos to the nucleus and is thus important for c-Fos induced transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation of c-Fos at Ser32 and Thr232 by Erk5 increases protein stability and nuclear localization. c-Fos plays an important role in many cellular functions and has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161