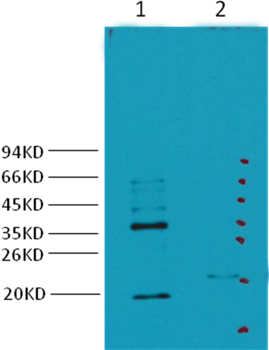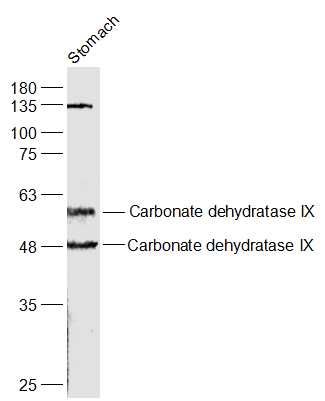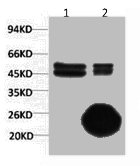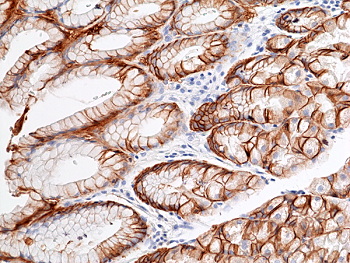
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human stomach tissue sections using anti-CA9 rabbit monoclonal antibody (RM486) at 1:100 dilution.
anti-CAIX (CA9), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM486)
REV-31-1378-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCA9
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CAIX (CA9), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM486)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM486
- Gene ID768
- Target nameCA9
- Target descriptioncarbonic anhydrase 9
- Target synonymsCAIX, MN, carbonic anhydrase 9, CA-IX, P54/58N, RCC-associated antigen G250, RCC-associated protein G250, carbonate dehydratase IX, carbonic anhydrase IX, carbonic dehydratase, membrane antigen MN, pMW1, renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen G250
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ16790
- Protein NameCarbonic anhydrase 9
- Scientific DescriptionCarbonic anhydrase (CA) is an enzyme that assists rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid, protons, and bicarbonate ions. It is abundant in all mammalian tissues. There are many genes that are inducible by hypoxia, via HIF-1 alpha. CAIX is one of the most inducible genes because of its stability and location within the membrane. Carbonic anhydrases have a widespread role in regulating pH in normal tissues, by regulating hydrogen ion (H+) flux. The pH is important in cell death under hypoxia, thus a blockade of CAIX results in increased cell death under hypoxia. Therefore, CAIX has become a reliable histochemical marker of hypoxia. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CAIX (CA9) (Carbonic Anhydrase 9). Source: Rabbit. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: A peptide corresponding to the C-terminus of human CAIX (CA9) (Carbonic Anhydrase 9). Applications: IHC, WB. Carbonic anhydrase (CA) is an enzyme that assists rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid, protons, and bicarbonate ions. It is abundant in all mammalian tissues. There are many genes that are inducible by hypoxia, via HIF-1 alpha. CAIX is one of the most inducible genes because of its stability and location within the membrane. Carbonic anhydrases have a widespread role in regulating pH in normal tissues, by regulating hydrogen ion (H+) flux. The pH is important in cell death under hypoxia, thus a blockade of CAIX results in increased cell death under hypoxia. Therefore, CAIX has become a reliable histochemical marker of hypoxia.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161