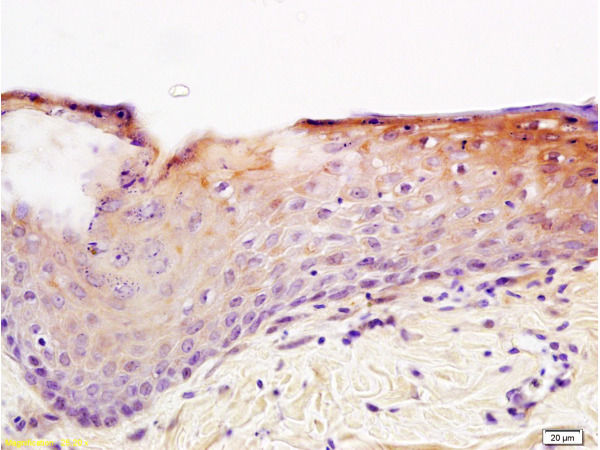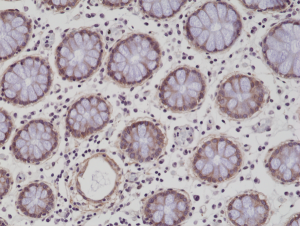
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human colon tissue sections using anti-CD29 rabbit monoclonal antibody (clone RM285) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-CD29 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM285)
REV-31-1169-00
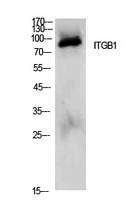
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetITGB1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD29 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM285)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM285
- Gene ID3688
- Target nameITGB1
- Target descriptionintegrin subunit beta 1
- Target synonymsCD29, FNRB, GPIIA, MDF2, MSK12, VLA-BETA, VLAB, integrin beta-1, glycoprotein IIa, integrin VLA-4 beta subunit, integrin beta 1, integrin, beta 1 (fibronectin receptor, beta polypeptide, antigen CD29 includes MDF2, MSK12), very late activation protein, beta polypeptide
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP05556
- Protein NameIntegrin beta-1
- Scientific DescriptionIntegrins are transmembrane proteins that mediate interactions between adhesion molecules on adjacent cells and/or the extracellular matrix (ECM). Integrins have diverse roles in several biological processes including cell migration during development and wound healing, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. Their activities can also regulate the metastatic and invasive potential of tumor cells. They exist as heterodimers consisting of alpha and beta subunits. Some alpha and beta subunits exhibit specificity for one another and may be designated as a VLA (very late antigen) member. Heterodimers often preferentially bind certain cell adhesion molecules, or constituents of the ECM. Although they have no catalytic activity, integrins can be part of multimolecular signaling complexes known as focal adhesions. CD29 (ITGB1; Integrin Subunit Beta 1; beta1 integrin subunit; GPIIa) is a 110 kDa cell surface glycoprotein that is widely expressed by a variety of cells including all leucocytes. CD29 forms non-covalently linked heterodimers with at least 6 different alpha chains (alpha1-alpha6, CDa-f) determining the binding properties of beta1 (VLA) integrins. CD29 is a cell adhesion molecule appearing on platelets, as the common Beta subunit of the very late activation antigen (VLA), and as a component of various protein complexes binding to extracellular matrix proteins. Decreased expression of CD29 correlates with acquiring multidrug resistance of tumor cells in the presence of anti-tumor drug. CD29 is up-regulated in leukocytes during emigration and extravascular migration and appear to be critically involved in regulating the immune cell trafficking from blood to tissue. Further, CD29 also regulates tissue damage and disease symptoms related to inflammatory bowel disease. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CD29 (Integrin beta-1). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Integrins are transmembrane proteins that mediate interactions between adhesion molecules on adjacent cells and/or the extracellular matrix (ECM). Integrins have diverse roles in several biological processes including cell migration during development and wound healing, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. Their activities can also regulate the metastatic and invasive potential of tumor cells. They exist as heterodimers consisting of alpha and beta subunits. Some alpha and beta subunits exhibit specificity for one another and may be designated as a VLA (very late antigen) member. Heterodimers often preferentially bind certain cell adhesion molecules, or constituents of the ECM. Although they have no catalytic activity, integrins can be part of multimolecular signaling complexes known as focal adhesions. CD29 (ITGB1; Integrin Subunit Beta 1; beta1 integrin subunit; GPIIa) is a 110 kDa cell surface glycoprotein that is widely expressed by a variety of cells including all leucocytes. CD29 forms non-covalently linked heterodimers with at least 6 different alpha chains (alpha1-alpha6, CDa-f) determining the binding properties of beta1 (VLA) integrins. CD29 is a cell adhesion molecule appearing on platelets, as the common Beta subunit of the very late activation antigen (VLA), and as a component of various protein complexes binding to extracellular matrix proteins. Decreased expression of CD29 correlates with acquiring multidrug resistance of tumor cells in the presence of anti-tumor drug. CD29 is up-regulated in leukocytes during emigration and extravascular migration and appear to be critically involved in regulating the immune cell trafficking from blood to tissue. Further, CD29 also regulates tissue damage and disease symptoms related to inflammatory bowel disease.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161